Global Change Data Encyclopedia
Botao Lake, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China
Gou, Z. J. Liu, F. G.*
Department of Geographic Sciences, Qinghai Normal University, Xining 810008, China
Keywords: Botao Lake; Qinghai-Tibet Plateau; Qinghai province; saltwater lake; data encyclopedia
Botao Lake is located in the hinterland of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, close to the border between Qinghai and Tibet. Its geo-location is 34°3′35″N-33°58′24″N, 89°53′31″E-90°0′37″E. It is 470 km from Lhasa city and 970 km from Qinghai Lake (Figure 1, Figure 2). Botao Lake is jujube-shaped, extending slightly from east to west. The elevation of the lake is 4,983 m above sea level, the catchment area is 71.23 km2 (2015), and the length of the lake coastline is 39.79 km (2015)[1]. Botao Lake belongs to Qinghai Province in administration[2].
|
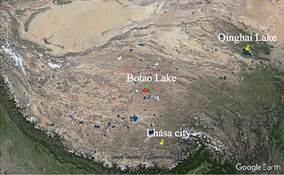
Figure 1 The geo-location of Botao Lake (Google Earth)
|
Botao Lake in the terrigenous fault zone between Zuerkenwula Mountain and Tanggula Mountain on the Qiangtang Plateau is a tectonic rift lake basin. The lake is surrounded by Zuerkenwula Mountain, Tanggula Mountain, Gaqiadirugang Mountain and Pregangri Mountain, and there are many large areas of sandy gravels in the lake beach. Taiping Lake, Taiping South Lake, and Xuelian Lake are located in the northwest and northeast of the lake shore respectively, and Yanzi Lake is located in the south of the lake shore. The lakeside is dotted with many small remnants of the lake, and there are sand dikes of the ancient lakeside in the east side, indicating that Botao Lake gradually shrinked after the lake prosperous period in the Quaternary. Botao Lake, Yanzi Lake, Nuoduocuo Lake, Maqiaocuo Lake, and Chibuzhangcuo Lake (also known as Mitijiangzhanmucuo Lake) are linked by Banglonglongba River, like beads. Hence, they are reputed as “Five Great Connected Lakes”[3].
|

Figure 2 The Geo-location of Botao Lake (.shp format)
|
Botao Lake is an inland saline lake, with an annual precipitation of about 200 mm. Water source are mainly from surface runoff, melt water of ice and snow, and infiltration of spring water. There are 4 surface runoffs flowing into the lake area. Among them, Lanli River, the upper reaches of Banglonglongba River, is the largest surface runoff, which is originated from the Meihua Snow Mountain (5,597 m) of Zuerkenwula Mountain, flowing from northeast to the west and into the Botao Lake from the north. The river course is curved and irregular. Before entering the lake, the river course is fan-shaped and separated into many branches. Lanli River flows out of the lake from its south and flows through the Jiejie River into Yanzi Lake. The upper reach flows through mountainous areas and the lower reach flow through valley basins. The topography is high in the southeast and low in the west, with the elevation of 4,988-5,597 m and the ice period of over 4-5 months. The other three rivers are intermittent streams. In the wet season, ice and snow melt water and atmospheric precipitation will inject into the lake from the south and southeast, respectively. The salinity of the lake water is 2.749 g/L, and the pH value is 8.6. It belongs to the sodium sulfate subtype inland huff and puff salt lake[4]. Botao Lake has a great impact on the surrounding ecological environment, including the formation of lakeside ecological type-alpine grassland type, which forms wetland together with the water body of Botao Lake. The main vegetation type in the wetland is Qinghai-Tibet Carex and Stipa purpurea alpine grassland. Such wetland provides the habitat environment for birds such as snow chickens, wild ducks, spotted geese, black-necked cranes and wild animals such as wild yak, wild donkey, blue sheep, argali, antelope, Tibetan antelope[5].
The Botao Lake dataset consists of 15 data files, which are archived in .shp[6] and .kmz[7] formats. The data size is 377 KB (compressed in 2 data files, 147 KB).
References
[1] Gou, Z. J., Liu, F. G. Botao Lake [DB/OL]. Global Change Research Data Publishing & Repository. DOI: 10.3974/geodb.2018.04.19.V1.
[2] Xi’an Surveying and Mapping General Station, Starmap Press. Map of Qinghai Province [M]. Beijing: Starmap Press, 1999.
[3] Sinomap Press. World Atlas [M]. Beijing: Sinomap Press, 1987: 22.
[4] Wang, S. M., Dou, H. S. China Lake Record [M]. Beijing: Science Press Ltd., 1998.
[5] Editorial Office of Encyclopedia of Rivers and Lakes in China. Encyclopedia of Rivers and Lakes in China: Section of River Basins in Southwest Region [M]. Beijing: China Water & Power Press, 2014.
Data Computing Environment
[6] ESRI. ArcGIS campus license of Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
[7] Google LLC. Google Earth Pro. 7.3.2.5481 (32-bit), hk.google.com.
URL for Data Downloading
http://www.geodoi.ac.cn/WebEn/doi.aspx?ID=932.
Or search through: http://www.geodoi.ac.cn.