Temporal
and Spatial Characteristics and Intraseasonal Variations of Summer
Precipitation Contribution Rates in the Haihe River Basin
He, L. Y.1,2 Hao, L. S.2* Cheng, S. J.2 Ma, N.2
1. China
Meteorological Administration Basin Heavy Rainfall Key Laboratory/Hubei Key
Laboratory for Heavy Rain Monitoring and Warning Research, Institute of Heavy
Rain, China Meteorological Administration, Wuhan 430205, China;
2. Tianjin
Climate Center, Tianjin 300074, China
Abstract: The summer
precipitation in the Haihe River Basin not only exhibits significant
interdecadal and interannual variations, but also shows obvious intraseasonal
variation characteristics in its spatial distribution. Based on the daily
precipitation data of 148 meteorological stations over the Haihe River Basin
from 1961 to 2015, the authors calculated the contribution of single station
precipitation to the Haihe River Basin total annual amount during summer, June,
July and August. Concurrently, according to the locations of the stations
within the various river systems of the Haihe River Basin, we calculated the
annual proportion of summer precipitation from nine river systems relative to
the total amount of the Haihe River Basin using the regional statistical
average method. Then the summer precipitation contribution rates dataset over
Haihe River Basin (1961-2015)
was developed. The dataset includes: (1) the contribution of precipitation to
total annual amount at 148 stations in the Haihe River Basin during the summer,
June, July and August from 1961 to 2015; (2) the contribution of precipitation
to total annual amount in the nine river systems in the Haihe River Basin
during the summer from 1961 to 2015. The dataset is archived in one excel file
with data size of 175 KB.
Keywords:
Haihe River
Basin; summer precipitation; contribution rate of precipitation; intraseasonal
change
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3974/geodp.2024.02.05
CSTR: https://cstr.escience.org.cn/CSTR:20146.14.2024.02.05
Dataset Availability Statement:
The dataset
supporting this paper was published and is accessible through the Digital Journal of
Global Change Data Repository at: https://doi.org/10.3974/geodb.2024.06.07.V1
or https://cstr.escience.org.cn/CSTR:20146.11. 2024.06.07.V1.
1 Introduction
The
Haihe River Basin is located in North China, with a dense population, playing a
pivotal role in China??s economic and social development. The water resources in
this region are relatively scarce[1], and the annual precipitation
is highly concentrated in the summer. Thus, the amount and distribution of
summer precipitation have an extremely important impact on the local climate,
agricultural and industrial production[2]. Additionally, the Haihe
River Basin is located on the northern edge of the East Asian summer monsoon
activities. The summer precipitation not only exhibits significant interannual
and interdecadal variability on the temporal scale[3,4], but also
shows significant regional differences in drought and flood conditions, with a
very uneven distribution of precipitation within the basin[5,6].
Previous studies
on the temporal and spatial variations of summer precipitation in the Haihe
River Basin have been extensive[7?C10], and most of these studies
directly used precipitation data, with few analyzing from the perspective of
precipitation contribution rates. This paper calculated the contribution of
single station precipitation to the Haihe River Basin??s total annual amount
during summer, June, July and August. Concurrently, according to the locations
of the stations within the various river systems of the Haihe River Basin, the
annual proportion of summer precipitation from nine river systems relative to
the total amount of the basin was calculated by using the regional statistical
average method. The study analyzes the distribution characteristics and
intraseasonal variations of the major contributing precipitation regions in the
Haihe River Basin from 1961 to 2015. This provides an important foundation and
climatic background for understanding the temporal and spatial patterns of
summer droughts and floods in this basin, and for improving summer precipitation
forecasting techniques.
2 Metadata of the Dataset
The
metadata of the Summer precipitation contribution rates dataset over Haihe
River Basin (1961?C2010)[11] is summarized in Table 1. It
includes the dataset full name, short name, authors, year of the dataset,
temporal resolution, spatial resolution, data format, data size, data files,
data publisher, and data sharing policy, etc.
3 Methods
Using
daily observation data from over 2,400 meteorological stations provided by the
National Meteorological Information Center, daily precipitation data from 148
complete observation stations located in the Haihe River Basin were selected
(Figure 1). The study period covers the summer months (June to August) from
1961 to 2015.
3.1 Algorithm
3.1.1 Contribution Rate of Station Precipitation
The
contribution rate of station precipitation is the proportion of the
precipitation at a single station during a specific period to the total amount
in the study area (in this article, the study area is the Haihe River Basin,
hereinafter referred to as the same) during the same period[13]. The
equation is as follows:
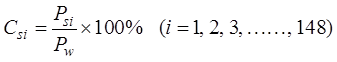 (1)
(1)
where, 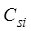 represents the
contribution rate of precipitation at the i-th station,
represents the
contribution rate of precipitation at the i-th station,  represents the i-th
station precipitation during a specific period, and
represents the i-th
station precipitation during a specific period, and  represents the
total
represents the
total
Table 1 Metadata summary of the summer precipitation contribution rates dataset over Haihe River Basin
(1961?C2015)
|
Items
|
Description
|
|
Dataset full name
|
Summer
precipitation contribution rates dataset over Haihe River Basin (1961?C2015)
|
|
Dataset short
name
|
SummerPrecipContribution_HaiheRB_1961-2015
|
|
Authors
|
He,
L. Y. L-4778-2016, China
Meteorological Administration Basin Heavy Rainfall Key Laboratory/Hubei Key
Laboratory for Heavy Rain Monitoring and Warning Research, Institute of Heavy
Rain, ChinaMeteorological Administration; Tianjin
Climate Center, heliyehly@163.com
Hao, L. S. Tianjin Climate Center, hls54515@163.com
Cheng, S. J. Tianjin Climate Center, chengshj08@lzu.edu.cn
Ma, N. Tianjin Climate Center, amsmaning@126.com
|
|
Geographical
region
|
Haihe River
Basin, China
|
|
Year
|
1961?C2015
|
|
Temporal
resolution
|
Year
|
|
Spatial resolution
|
Station, River
System
|
|
Data format
|
.xlsx
|
|
|
|
Data size
|
175 KB
|
|
|
|
Data files
|
(1) contribution of
precipitation to total annual amount at 148 stations in the Haihe River Basin
during the summer from 1961 to 2015; (2) contribution of precipitation to total
annual amount at 148 stations in the Haihe River Basin during June, July and
August from 1961 to 2015; (3) contribution of precipitation to total annual
amount in the nine river systems in the Haihe River Basin during the summer
from 1961 to 2015
|
|
Foundations
|
China Meteorological
Administration Basin Heavy Rainfall Key Laboratory (2023BHR- Y05); Haihe
River Basin Meteorological Technology Innovation Fund (HHXM202408); Ministry of Science and Technology of P. R.
China (2018YFA0606302, GYHY201506001-1)
|
|
Computing
environment
|
NCAR Command
Language (NCL); Fortran; Microsoft Excel
|
|
Data publisher
|
Global Change Research Data Publishing & Repository,
http://www.geodoi.ac.cn
|
|
Address
|
No. 11A, Datun
Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing 100101, China
|
|
Data sharing policy
|
(1) Data are openly available and can be free downloaded via the
Internet; (2) End users are encouraged to use Data subject to citation; (3) Users, who are by definition also
value- added service providers, are welcome to redistribute Data subject to written permission
from the GCdataPR Editorial Office and the issuance of a Data redistribution license; and (4) If Data are used to compile new datasets, the ??ten percent
principal?? should be followed such that Data
records utilized should not surpass 10% of the new dataset contents, while
sources should be clearly noted in suitable places in the new dataset[14]
|
|
Communication and
searchable system
|
DOI, CSTR, Crossref, DCI, CSCD, CNKI, SciEngine, WDS,
GEOSS, PubScholar, CKRSC
|
precipitation
in the Haihe River Basin during the same period as  .
.
3.1.2 Contribution Rate of River System Precipitation
The
contribution rate of river system precipitation refers to the proportion of the
average precipitation in each river system during a specific period to the
total amount in the study area during the same period[14,15]. The eaqution
is as follows:
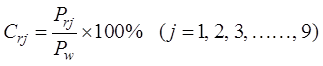 (2)
(2)
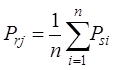 (3)
(3)
where, 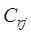 represents the precipitation contribution rate of the j-th river system,
represents the precipitation contribution rate of the j-th river system,  represents the
average precipitation of the j-th river system
during a specific period,
represents the
average precipitation of the j-th river system
during a specific period,  represents the
total precipitation of the Haihe River Basin during the same period as
represents the
total precipitation of the Haihe River Basin during the same period as  ,
,  represents the
precipitation of the i-th station located in the
j-th river system, and n represents the total number of stations
located in the j-th river system.
represents the
precipitation of the i-th station located in the
j-th river system, and n represents the total number of stations
located in the j-th river system.
By applying the
above method, it is possible to more clearly reflect the contribution of
precipitation from different regions or different river systems to the total
basin amount during different periods.
3.2 Data Processing
(1)
Using the daily precipitation data of 148 meteorological stations in the Haihe
River Basin, the annual precipitation for each station in summer, June, July,
and August was calculated from 1961 to 2015.
(2) According to
the Equation 1, the precipitation contribution rates of the annual summer and
monthly (June to August) periods were calculated for 148 stations in this
basin.
(3) Based on the
distribution of meteorological stations within the nine river systems in the
Haihe River Basin (Figure 1), the annual summer precipitation contribution
rates for each river system were calculated using the Equations 2 and 3.
(4) The
aforementioned calculation results were used to derive the dataset of summer
precipitation contribution rates over the Haihe River Basin from 1961 to 2015.
![??????:
Figure 1 Distribution map of meteorological stations and river systems in the Haihe River Basin[6]](https://geodoi.ac.cn/DOIPaper/ENHTML/2024139402\202402139405.files/image022.png) 4 Data Results and
Validation
4 Data Results and
Validation
4.1 Data Composition
The
dataset of summer precipitation contribution rates over the Haihe River Basin
from 1961 to 2015[11] includes: (1) contribution
of precipitation to total annual amount at 148 stations in the Haihe River
Basin during the summer from 1961 to 2015; (2) contribution of precipitation to
total annual amount at 148 stations in the Haihe River Basin during June, July
and August from 1961 to 2015; (3) contribution of precipitation to total annual
amount in the nine river systems in the Haihe River Basin during the summer
from 1961 to 2015. The dataset is archived in one excel file with data size of
175 KB.
4.2 Data Results
4.2.1 Spatial Distribution and Intraseasonal Variations of Summer
Precipitation Contribution Rates in the Haihe River Basin
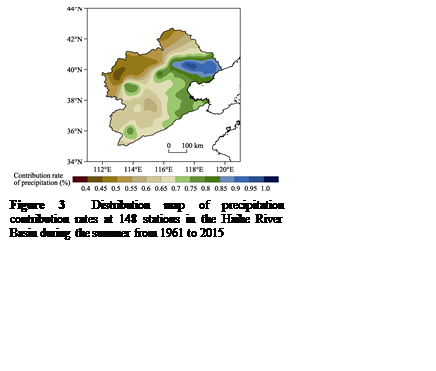
From
the distribution of summer precipitation contribution rates in the Haihe River
Basin (Figure 3), it can be observed that the contribution rates gradually
decrease from east to west. The high value areas are located in the
northeastern part of the basin, specifically in the lower reaches of the Luanhe
River and the Beisan River. The low value areas are found on the western side
of the basin, primarily in the Yongding River.
To further study the intraseasonal variation characteristics of
summer precipitation contribution rates in the Haihe River Basin, an analysis
was conducted on the spatial distribution of
the high value areas of precipitation contribution rates for each month of summer
at various
 stations[6], as shown in Figure 4. It can be
seen that in June, the main contribution area of precipitation is located in
the northeastern part of the basin. In July, it shifts to the eastern and
southern parts of the basin. By August, the main contribution area not only
includes the eastern part of the basin but also sees the July southern contribution
area move northward to the central part of the basin, forming a northeast-southwest oriented high value belt. Consistently, throughout the three
summer months, the main contribution areas of precipitation always include the
high value center in the northea stern part of the Haihe River Basin.
stations[6], as shown in Figure 4. It can be
seen that in June, the main contribution area of precipitation is located in
the northeastern part of the basin. In July, it shifts to the eastern and
southern parts of the basin. By August, the main contribution area not only
includes the eastern part of the basin but also sees the July southern contribution
area move northward to the central part of the basin, forming a northeast-southwest oriented high value belt. Consistently, throughout the three
summer months, the main contribution areas of precipitation always include the
high value center in the northea stern part of the Haihe River Basin.
4.2.2 Temporal Variations of Summer Precipitation Contribution Rates in the
Haihe River Basin
Based
on the statistics of summer precipitation contribution rates for the nine
river systems in the Haihe River Basin, the time series from 1961 to 2015 for
each river system is presented in Figure 5. It can be observed that the summer
precipitation contribution rates of each river system exhibit significant interannual
variability. From the interannual average results, the Luanhe River and Beisan
River have the highest average precipitation contribution rates, both exceeding
12.5%. They are followed by the Tuhaimajia River and the Haihe River
Mainstream, with average precipitation contribution rates both above 11.5%. The
Yongding River has the lowest average precipitation contribution rate, at only
8.0%, making it the only river system with an average precipitation
contribution rate below 10% in the Haihe River Basin.
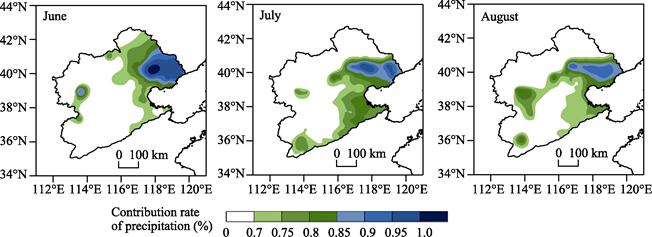
Figure 4 Distribution
maps of high value areas of monthly precipitation contribution rates in the
Haihe River Basin during the summer from 1961 to 2015
On the decadal
scale, the summer precipitation contribution rates in the Luanhe River, Beisan
River, Daqing River, Heilonggang River, and the Haihe River Mainstream within
the basin show a decreasing trend, with the Haihe River Mainstream exhibiting a
more pronounced decline. In contrast, the summer precipitation contribution
rates in the Yongding River, Ziya River, Zhangwei River, and Tuhaimajia River
show an increasing trend, particularly in the southern part of the basin where
the Zhangwei River and Tuhaimajia River exhibit a more significant upward
trend.
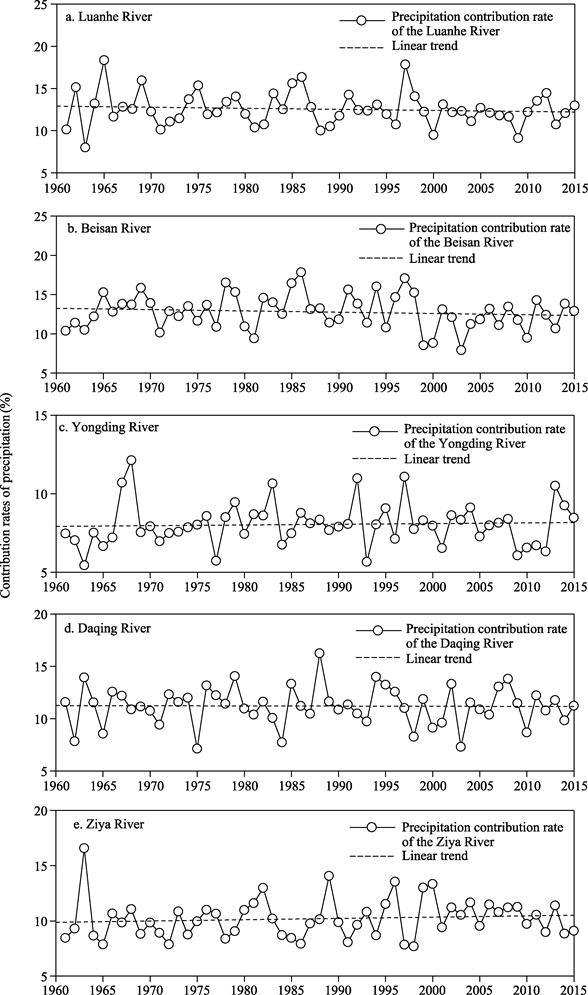
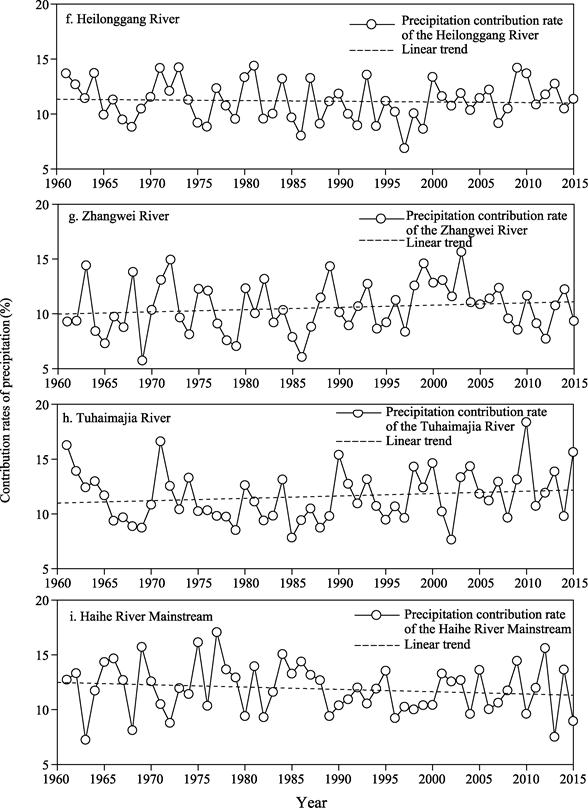
Figure 5 The time
series of precipitation contribution rates for nine river systems in the Haihe
River Basin during the summer from 1961 to 2015
5 Discussion and Conclusion
The
Haihe River Basin is both a climate vulnerable area prone to drought and
flooding and a region with relatively scarce water resources. Precipitation is
one of the important sources of surface water and shallow groundwater recharge
in this basin. 60%-70% of the annual precipitation in the
Haihe River Basin comes from summer precipitation. By calculating the annual
precipitation contribution rates of stations and river systems within the Haihe
River Basin during the summer, June, July and August from 1961 to 2015, this
study investigates the evolution patterns of summer precipitation in the Haihe
River Basin from the perspective of precipitation contribution rates. It
analyzes the temporal and spatial characteristics and intraseasonal variations
of the areas that mainly contribute to summer precipitation in this basin. The
results show that the high value center of summer precipitation contribution
rates is primarily located in the northeastern part of the basin, particularly
in the downstream areas of the Luanhe River and the Beisan River. This high
value center remains stable throughout the summer months and is a key area of
focus for summer precipitation research and flood prevention efforts. The
summer precipitation contribution rates data for the Haihe River Basin
developed in this study provides a crucial data foundation for understanding
the temporal and spatial distribution unevenness of drought and flood within
this basin. The data calculation methods and analysis conclusions also offer
references for future research on summer precipitation in the Haihe River Basin
Author Contributions
He,
L. Y. and Hao, L. S. designed the algorithms of dataset. He, L. Y., Cheng, S.
J. and Ma, N. contributed to the data processing and analysis. He, L. Y. wrote
the data paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The
authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
[1]
Huang,
R. H., Xu, Y. H., Zhou, L. T. The interdecadal variation of summer
precipitations in China and the drought trend in North China [J]. Plateau
Meteorology, 1999, 18(4): 465-476.
[2]
Hao, L. S., Ding, Y. H.
Progress of precipitation research in North China [J]. Progress in Geography,
2012, 31(5): 593-601.
[3]
Fan, K., Lin, M. J., Gao, Y. Z.
Predicting flood season precipitation in North China using the interannual
increment method [J]. Science in China (Series D: Earth Sciences), 2008, 38(11): 1452-1459.
[4]
Liu, H. W., Ding, Y. H. The
interdecadal variability of summer precipitation over North China [J]. Quarterly
Journal of Applied Meteorology, 2011, 22(2): 129-137.
[5]
Zhao, C. G., Li, Z, C. The
regionalization and temporal characteristic of rainfall anomalies in North
China during summer [J]. Quarterly Journal of Applied Meteorology, 2012,
23(6): 641-649.
[6]
He, L. Y., Cheng, S. J., Ma,
N., et al. Intraseasonal evolution of the key areas of precipitation in
the Haihe River Basin and quantitative analysis of its associated atmospheric
circulation during summer [J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2020, 75(1): 41-52.
[7]
Lu, R. Y. Interdecadal
variations of precipitations in various months of summer in North China [J]. Plateau
Meteorology, 1999, 18(4): 509-519.
[8]
Xu, G. Y., Yang, X. Q., Sun, X.
G. Interdecadal and interannual variation characteristics of rainfall in North
China and its relation with the northern hemisphere atmospheric circulations
[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2005, 48(3): 511-518.
[9]
Lu, R. Y. Interannual variation
of flood season precipitation in North China and sea surface temperature in the
Equatorial Eastern Pacific [J]. Science Bulletin, 2005, 50(11): 1131-1135.
[10]
Hao, L. S., He, L. Y., Ma, N. A
study on the relationship between interannual summer precipitation anomalies in
North China and atmospheric dynamics and water vapor conditions in the recent
60 years [J]. Transactions of Atmospheric Sciences, 2023, 46(4): 587-599.
[11]
He, L. Y., Hao, L. S., Cheng,
S. J., et al. Summer precipitation contribution rates dataset over Haihe
River Basin (1961-2015) [J/DB/OL]. Digital Journal of Global Change Data Repository,
2024. https://doi.org/ 10.3974/geodb.2024.06.07.V1. https://cstr.escience.org.cn/CSTR:20146.11.2024.06.07.V1.
[12]
GCdataPR Editorial Office.
GCdataPR data sharing policy [OL]. https://doi.org/10.3974/dp.policy.2014.05 (Updated
2017).
[13]
Shen,
Q., Zhang, S. X., Zhao, J. H., et al. Contribution of typhoon over
coastal waters to summer rainfall in eastern China [J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2013, 62(18): 189-201.
[14]
Sun, Y., Gao, J. Q., Yang, X.
G. Seasonal variation about the occurrence frequency of different types of
precipitation and their relative contribution over northwest China [J]. Chinese
Journal of Agrometeorology, 2019, 40(8): 489-501.
[15]
Jiang, L. X., Li, F. H., Wang,
Q. Q., et al. Study on abnormal rainfall characteristics and its
contribution to total precipitation in summer in Heilongjiang Province [J]. Journal
of Northeast Agricultural University, 2019, 50(3): 86-96.