Xu,
E. Q.
Key
Laboratory of Land Surface Pattern and Simulation, Institute
of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences,
Beijing 100101, China
Abstract: The challenges from agricultural resources and environment
have become increasingly prominent in China, but vary considerably by region.
The dataset of agricultural resource
and environment zoning of China was produced according to the
agricultural production characteristics, suitability and environmental challenges. It is divided the specific regional spatial
units of territories into different agricultural
resource and environmental zones
of China. Using the county as the basic mapping unit, the zoning is consisted of two levels.
The ten first-level zones were identified
according to regional differences in climate and geotectonic characteristics at
the macro scale. Next, fifty-seven second-level zones were differentiated
according to water resources, land resources, and environmental conditions. The
zoning method is a dominant factor method based on comprehensive analysis of
agricultural resources and environmental factors. The naming of the zones is
based on the principles of simplicity, clarity and popularity. The first-level
zones are mainly named according to the physical geographical location, and the
naming of the second-level districts is in conjunction with geographic location
and landform types.
Keywords: resource and
environment; zoning; regional difference; China
Dataset Available
Statement:
The dataset supporting this paper was published and is accessible through
the Digital Journal of Global Change Data
Repository at: https://doi.org/10.3974/geodb.2021.02.07.V1.
1 Introduction
During the last half century, the
agricultural development in China successfully solved the problem of feeding
1.4 billion people. However, agricultural environmental pollution has intensified,
and agricultural resources and the environment are generally overloaded, which have
been a substantial constraint on sustainable agricultural development[1].
The vast territory presents significant differences in terrain in China, such
as water and heat conditions, and different levels of regional socio-economic
development. These have resulted in different constraints on agricultural
resources and the agricultural environment in the different regions, with
diverse reasons, types, and degrees of the regional constraints. Following certain
principles and indicators, the ??Dataset of agricultural resource and
environment zoning of China?? was developed. This dataset diagnoses resource and
environmental challenges and limiting factors in different districts and reveals
the regional differentiation of agricultural production. It characterizes the
agricultural production conditions, resource types and their combinations and
existing problems in various regions of the country, as well as their favorable
and unfavorable effects on agricultural production. The dataset describes
similarities and differences in agricultural resource and environment problems
according to their formation process, types and characteristics of problems in
different zones in China. The dataset could be a reference in recognizing
regional agricultural production and the rational use and protection of
agricultural resources and environment in accordance with local conditions,
which maintains and improves the health and sustainability of agricultural
ecosystem of China.
2 Metadata of the Dataset
The name, authors, geographical regions, data
date, temporal resolution, spatial resolution, data files, data publisher, and
data sharing policy of the Dataset of agricultural resource and environment
zoning of China[2] are shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Metadata summary of the Dataset of
agricultural resource and environment zoning of China
|
Items
|
Description
|
|
Dataset full name
|
Dataset of agricultural resource and environment zoning of China
|
|
Dataset short name
|
ChinaAgriREZone
|
|
Authors
|
Xu, E.Q. U-9329-2017, Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural
Resources Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, xueq@igsnrr.ac.cn
|
|
Geographical region
|
China
|
Data date
|
2018
|
spatial resolution
|
1:1 million
|
|
Data format
|
.shp
|
Data size
|
48.8 MB
|
temporal resolution Year
|
|
Data files
|
A group of 7 documents, including 10 first-level zones and 57
second-level zones of agricultural resource and environment of China
|
|
Foundation(s)
|
Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDA19040305??
|
|
Data computing environment
|
ArcGIS, Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research,
Chinese Academy of Sciences platform
|
|
Data publisher
|
Global Change Research Data Publishing & Repository http://www.geodoi.ac.cn
|
|
Address
|
No. 11A, Datun Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing 100101, China
|
|
Data sharing policy
|
Data from
the Global Change Research Data Publishing & Repository includes metadata, datasets (in the Digital Journal of Global Change Data Repository), and
publications (in the Journal of Global Change Data & Discovery). Data sharing policy
includes: (1) Data are openly available and can be free downloaded via the
Internet; (2) End users are encouraged to use Data subject to
citation; (3) Users, who are by definition also value-added service
providers, are welcome to redistribute Data subject to written permission
from the GCdataPR Editorial Office and the issuance of a Data redistribution
license; and (4) If Data are used to compile new
datasets, the ??ten per cent principal?? should be followed such that Data
records utilized should not surpass 10% of the new dataset contents, while
sources should be clearly noted in suitable places in the new dataset[3]
|
|
Communication and searchable system
|
DOI, DCI, CSCD, WDS/ISC, GEOSS, China GEOSS, Crossref
|
3 Data Development Methods
3.1 Zoning Principle
The division of Agricultural Resource and Environment Zoning of China
is based on the
regional principles of similarity and difference, which integrate the following
characteristics in carrying out the division of regions.
(1) Consistency of agricultural resource and
environment system. The agricultural resource and environment system is the
basis of the zoning formation and differentiation. Agricultural production depends
on the agricultural resource and the environment elements. The differences in
the agricultural resource and environment system structure will inevitably lead
to differences in the structure of agricultural production and the agricultural
resource and environment zones.
(2) Consistency of agricultural production
structure and function. The agricultural production structure is not only
affected by the regional agricultural ecological environment structure, but is
also restricted by the regional socio-economic structure and technical conditions.
The two are comprehensively reflected in the agricultural production structure.
Moreover, the agricultural production structure is closely related to the
production development direction: the same agricultural production structure,
the agricultural production direction is basically the same.
(3) Consistency of agricultural productivity
level. System productivity is a comprehensive indicator that reflects the
status of the agricultural resource and environment system. Thus, it is
necessary to integrate the factors, such as climate, soil fertility, water
supply, and management levels in the system result in the productivity level.
(4) Consistency of agricultural environment
problems. The environmental problems in the agricultural ecosystem restrict the
balance and development of the system, it may lead to the reduction of system
functions and even the collapse of the entire system. Within each zone, the
dataset puts forward countermeasures to the problems to make improvements and
realize the normal exertion, virtuous circle and sustainability of system functions.
(5) Spatial continuity of each zone. A zone
is mainly represented in the interaction between adjacent geographic
sub-systems with similar agricultural resources and environment. Except for a
few discontinuities caused by administrative demarcation, the emergence of
enclaves, i.e. non-continuous spaces, should be minimized.
3.2 Partition Process
There are several products from zoning
program of China, such as Integrated Physical Zoning[4] and
Integrated Agricultural Zoning[5], which are the main reference materials
for this dataset production. In addition, 1:1 million Land Resource Map of
China[6], 1:1 million Vegetation Map of China[7],
Landform Map of China in 1:4 million scale[8] and the National
Ecological Function zoning[9] are additional zoning references.
Based on the division of agricultural
resource factors, agricultural environmental issues and agricultural planting
structure, this research aims to flesh out the division of first-level and second-level
agricultural resource and environment zones of China??s territories. The zoning method is
the dominant factor method based on the comprehensive analysis of agricultural
resource and environment factors. The division of zones into two levels is
based on the following standards:
(1) First-level zones are mainly divided by
climatic condition and geological structure, including (a) basic structure of
the tectonic structure; and (b) agricultural resource endowment, i.e.,
agricultural production potential, which mainly includes regional hydrothermal
conditions and matching relationships, and also involves the regional distribution
of cropland and the level of agricultural production input.
(2) Second-level zones are mainly divided
based on cropland resource factors and environment problems including (a)
cropland resource factors, such as cropland composition, resource matching and
limiting factors; (b) cropland environmental quality, including land element
quality, mainland degradation and pollution problems; and (c) medium landform
types, including mountains, hills, plains and their combinations.
The naming of zones is based on the
principles of simplicity, clarity and popularity. The first-level
zones are mostly named according to the physical geographical location. The naming
of the second-level districts is in conjunction with geographic location and
landform types.
4 Data Results
4.1 Data
Sources
The dataset of agricultural resource and
environment zoning of China is mainly analyzed and drawn based on China??s county-level administrative
boundary data and socio-economic statistics data (2015)1.
4.2 Data
Results
Based on the
county boundaries data as the spatial data, 10 regions were identified at the first-level
zoning system, marked by Roman numerals I, II, and to X, respectively. They are
the Northeast China Region, Inner Mongolia along the Great Wall Region,
Huang-Huai-Hai Region, Loess Plateau Region, Northwest Arid Region, Plain and
Hilly in the Middle and Lower Reaches of Yangtze River Region, Hilly and
Mountain in the south of Yangtze River Region, Southeast China Region,
Southwest China Region, and Qinghai-Tibet Plateau Region. In addition to the
first-level zones, fifty-seven second-level zones are divided according to
differences in land resources and numbered by Arabic numerals 1, 2, 3, etc.
(Figure 1). The attributes of this dataset are mainly the serial numbers and
names of agricultural resource and environment zoning of China, including
the first-level and second-level zones (Table 2).
Northeast China Region (??)
includes the three provinces of Liaoning, Jilin, Heilongjiang and eastern Inner
Mongolia. The area is about 1.227,5 million km2, accounting for
approximately 12.79% of the country??s territory area. This zone is currently
the only region in China that can export a large amount of commercial grains,
and it is also the most concentrated area of forest
resources in the country. The Songnen Plain Zone and the Sanjiang Plain Zone
have a high quality of cropland resources, which plays an important role in the
national food security. The Greater Khingan Mountain Zone, Lesser Khingan
Mountain Zone and Baekdu Mountain Zone are the main forested areas in this zone.
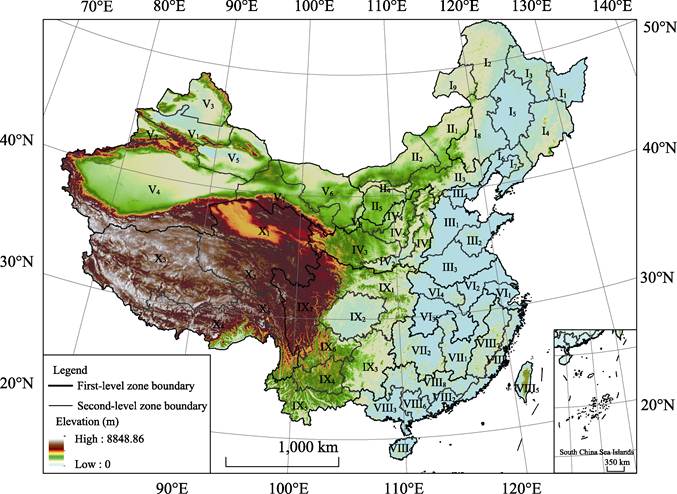
Figure 1 Map of agricultural resource and
environment zones of China
1 Resource and Environment
Science and Data Center. http://www.resdc.cn/data.aspx?DATAID=202.
Table 2 Serial numbers and names of agricultural
resource and environment zoning of China
|
Serial number
of first-level zone
|
Name of first-
level zone
|
Serial number of second-
level zone
|
Name of second-level zone
|
|
??
|
Northeast
China Region
|
??1
|
Sanjiang Plain Zone
|
|
??2
|
Greater Khingan
Mountain Zone
|
|
??3
|
Lesser Khingan
Mountain Zone
|
|
??4
|
Baekdu Mountain Zone
|
|
??5
|
Songnen Plain Zone
|
|
??6
|
Liaoning Plain and Hilly Zone
|
|
??7
|
Central and Southern Liaoning Zone
|
|
??8
|
Western Liao River Zone
|
|
??9
|
Hulunbuir Grassland Zone
|
|
??
|
Inner Mongolia along the Great Wall Region
|
??1
|
Eastern Xilin Gol Grassland Zone
|
|
??2
|
Western Xilin
Gol Desert Steppe Zone
|
|
??3
|
Yin Mountain along the Great Wall Zone
|
|
??4
|
Hu-Bao Hetao Zone
|
|
??5
|
Ordos Plateau Zone
|
|
??
|
Huang-Huai-Hai
Region
|
??1
|
North China
Plain Zone
|
|
??2
|
Shandong Hill Zone
|
|
??3
|
Huang-Huai Plain Zone
|
|
??4
|
Bohai Gulf Zone
|
|
??
|
Loess Plateau Region
|
??1
|
Jin-Yu
Earth-rock Mountain Zone
|
|
??2
|
Fen-he and Wei-he Valley Zone
|
|
??3
|
Loess Plateau Gully Zone
|
|
??4
|
Hill and Sandy Land in Northern Shaanxi and Eastern Ningxia
Zone
|
|
??5
|
Loess Hilly and Gully Zone
|
|
??
|
Northwest Arid Region
|
??1
|
North Slope of
Tianshan Mountain Zone
|
|
??2
|
Yili River Basin Zone
|
|
??3
|
Ertix-Ulungur River Basin Zone
|
|
??4
|
Tarim Basin Zone
|
|
??5
|
Eastern Xinjiang Zone
|
|
??6
|
Alxa-Ejina Plateau Zone
|
|
??7
|
Hexi Corridor Zone
|
|
??8
|
Yinchuan Plain Zone
|
|
??
|
Plain and Hilly in the Middle and lower
reaches of Yangtze River Region
|
??1
|
Yangtze River
Delta Zone
|
|
??2
|
Jianghuai Zone
|
|
??3
|
Plain of Mid-Yangtze River Zone
|
|
??4
|
Plain and Hill of Henan, Anhui and Hubei Zone
|
|
??
|
Hilly and Mountain in the south of
Yangtze River Region
|
??1
|
Middle and Upper
Gan River Basin Zone
|
|
??2
|
Middle and Upper Xiang River Basin Zone
|
|
??
|
Southeast China
Region
|
??1
|
Coastal Plain and Hill in Zhejiang, Fujian and Guangdong
Zone
|
|
??2
|
Pearl River Delta Zone
|
|
??3
|
Hill of Western Guangong and Southern Guangxi Zone
|
|
??4
|
Hainan Island Zone
|
|
??5
|
Taiwan Island Zone
|
|
??6
|
Coastal Hill in Guangong and Guangxi Zone
|
|
??7
|
Hill and Mountain in Zhejiang and Fujian Zone
|
|
??8
|
Hill and Mountain in Northern Guangdong and Guangxi Zone
|
|
??
|
Southwest China
Region
|
??1
|
Qinling, Funiu,
Eastern Sichuan Mountains Zone
|
|
??2
|
Sichuan Basin Zone
|
|
??3
|
Karst Hill and Mountain in Guizhou and Guangxi Zone
|
|
??4
|
Yunnan Plateau Zone
|
|
??5
|
Hill and Mountain in Southern Yunnan Zone
|
|
??6
|
Mountain in upper reaches of Yangtze River Zone
|
|
??7
|
Garz-Ngaw Plateau Zone
|
|
??
|
Qinghai-Tibet
Plateau Region
|
??1
|
Qaidam Basin
Zone
|
|
??2
|
Sanjiangyuan and Surrounding Zone
|
|
??3
|
Northern Tibetan Plateau Zone
|
|
??4
|
Midstream of Yarlung Zangbo and Two Tributaries in Southern
Tibet Zone
|
|
??5
|
Hengduan Mountain Zone
|
Inner Mongolia along the Great Wall Region
(??) is located to the east of Helan Mountain and north of Yinshan Mountain. The
scope of its administrative reach includes northwestern areas of Beijing and
Hebei, central and northern Inner Mongolia, and western Liaoning. It is a vast
area and sparsely populated, with a territory area of about 536,200 km2,
accounting for about 5.59% of the country??s area. Almost all of this area is
located in the temperate grassland climate, containing the semi-arid and arid
grassland areas. It is an important pastoral area and farming-pastoral area in
China. The Hu-Bao Hetao Zone is the main agricultural area in the region. The
Ordos Plateau Zone and Western Xilin Gol Desert Steppe Zone have poor
agricultural resources and environmental conditions.
Huang-Huai-Hai Region (??) is located south of
the Great Wall, north of the Huaihe River, and east of Taihang Mountain. The
scope of its administrative reach covers Tianjin, Shandong, southern Beijing,
southeastern Hebei, northeastern Henan, Anhui, and northern Jiangsu. Its territory
area is about 443,700 km2, accounting for 4.62% of the country??s
area. The Huang-Huai-Hai region is densely populated and has the largest plain
in China. It is composed of plains, including the North China Plain, Shandong
Hills, and Huanghuai Plain. It is an important production base for
grain?Despecially winter wheat, cotton, oil, meat, and fruit in China.
Loess Plateau Region (??) is
located west of Taihang Mountain, east of Qinghai Riyue Mountain, north of
Qinling Mountains, and south of the Great Wall. Its scope of administrative
reach includes Shanxi, western Henan, most of Shaanxi, northeastern Gansu,
eastern Qinghai, and southeastern Ningxia. Its territory area is about 496,800
km2, accounting for about 5.18% of the country??s area. It is the
region with the most concentrated and largest coverage of loess distribution in
the world. It is also one of the high-quality production areas of wheat, corn,
and fruits in China. The Fen-he and Wei-he Valley Zone is a high-quality
agricultural area, but other zones within this region have considerable
agricultural resource and environment problems.
Northwest Arid Region
(??) is
located to the west of Helan Mountain, north of Kunlun Mountain and Qilian
Mountain, and includes in its administrative scope Xinjiang, central and
western Gansu, western Inner Mongolia, and northwestern Ningxia. The territory
area is about 2.209 million km2, accounting for about 23% of the
country??s area. This region is rich in light and heat resources but has an
extremely dry climate with sparse vegetation across its landscape. The
agriculture here is oasis irrigated agriculture and has the largest
high-quality cotton base in China. Except for the limited areas in the Yili
River Basin, the northern and southern slopes of the Tianshan Mountain, the
Hexi Corridor, and the Yinchuan Plain, the agricultural resources and
environmental conditions in this region are relatively poor.
Plain and Hilly in the Middle and lower
reaches of Yangtze River Region (??) is located south of the Huaihe River and
east of the western Hubei mountains. Its administrative scope includes
Shanghai, southern Jiangsu, northeastern Zhejiang, central Anhui, northwestern
Jiangxi, southwestern Henan, eastern Hubei, and northeastern Hunan. Its
territory area is about 375,600 km2, which occupies about 3.91% of
the country??s total territory area. The region is a traditional base of
commercial grain, cotton, oil and freshwater aquaculture production. This
region is dominated by plains, consisting of the plains in the middle and lower
reaches of the Yangtze River and several mountains in northern Hubei and
southern Henan. Plains include the Jianghan Plain, Dongting Lake Plain, Poyang
Lake Plain, Jianghuai Region, Lixiahe Plain, Taihu Plain and Yangtze River
Delta. The light, water and heat conditions are well suitable for agricultural
production. The golden waterway of the Yangtze River runs through the whole
region and yields rich river runoff. The region is a rare area in China in that
it has good matching of water, heat and resources, with suitable land development
and ability to utilize it as well as high agricultural production.
Hilly and Mountain to the south of Yangtze River
Region (??) refers to the low mountain
and hilly area to the south of Dongting Lake Plain and Poyang Lake Plain, north
of Nanling Mountain, east of Xuefeng Mountain, and west of Wuyi Mountain. The
territory area is about 358,100 km2, accounting for about 3.73% of the
country??s total area. This region is an important base of rice production and
fast-growing, high-yielding forests in China. It is also known
for its production of tropical fruits and vegetables in China. With complex landforms
of plains, low hills, basins and mountains, this region forms a unique
three-dimensional agricultural model.
Southeast China Region (??) includes
the administrative scopes of southeastern Zhejiang, Fujian, Guangdong, most of
Guangxi, Hainan and Taiwan. Its territory area is about 653,500 km2, accounting for
about 6.81% of the country??s area. This region is suitable for multiple
agricultural products. The production of rice, sucrose, peanuts, mulberry,
hemp, tea, fruits and vegetables takes place here and is important in China.
More importantly, this region is the most vital for sucrose production in
China, and also an important base of rice production and the most suitable base
for the tropical and subtropical crop development. The sucrose production is
concentrated in the Hill of Western Guangong and Southern Guangxi Zone, and the
tropical crop productions are mainly distributed in Hainan Island Zone and
Taiwan Island Zone. The agricultural resources and environmental conditions in
the plain areas are also relatively good in the region.
Southwest China Region (??) is composed of
the Sichuan Basin, the Qinba Mountains, the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau, and the
Western Guizhou Karst Area. The administrative scope covers eight provinces
(Municipality), including Sichuan, Chongqing and Guizhou, most areas of Yunnan,
southern Shaanxi and Gansu, eastern Hubei and the western edge of Henan. The
territory area is about 1,333,700 km2, accounting for about 13.89%
of the country??s area. This region has the most complex and diverse physical
conditions and agricultural resources in China, with limited flatland resources
and significant variation in elevation. It has the second largest forest district
in China. The Sichuan Basin Zone and the Hill and Mountain in Southern Yunnan
Zone are important agricultural production areas in China.
Qinghai-Tibet Plateau Region (??) starts from the Himalayas
in the south, the Pamirs and Karakoram Mountains in the west, and the Yulongxue
Mountain, Daxue Mountain, Jiajin Mountain, Qionglai Mountain, and southeastern
foothills of the Min Mountain in the east. Its east and northeast boundary
borders the western section of Qinling Mountains and Loess Plateau. The
territory area is about 1,965,900 km2, accounting for about 20.48%
of the country??s area, which is the largest region among the ten first-level regions.
This region is located in the uppermost step of China??s three geomorphological
steps from west to east, forming a high-cold agriculture and animal husbandry
adapted to a low-oxygen environment. The area of cropland in this region only
accounts for 0.78% of the country??s total area. The water resources are rich
here, but the natural environment is extremely harsh, which has resulted in a
landscape dominated by pastures and a very fragile agricultural system.
4.3 Data
Verification
The first-level zones of ??Dataset of agricultural resource
and environment zoning of China?? are mainly divided according to the climatic
conditions of and regional differences in geotectonics related to China??s
agricultural production. The aforementioned zoning divisions have not changed
much since the dataset??s compilation, so the boundary of the first-level zone
is generally stable within the dataset. The second-level zones are mainly
divided by the characteristics and problems of China??s agricultural resource
and environment in the year 2015. With the development of regional agriculture,
the resource and environmental problems may change, and the scope of
agricultural zoning for the second-level zones can be revised accordingly.
5 Discussion and Conclusion
Based on the regional differentiation of
agricultural resources and environment in China, China??s territory is divided
into 10 first-level zones and 57 second-level zones, and the resulting of ??Dataset of agricultural resource and environment
zoning of China?? was produced. It should be noted that the division of agricultural resource and
environment zones is to guide regional agricultural production, development,
and distribution. This call for a focus on the social and economic factors, and
thus the zones are produced with the administrative county as the basic unit.
Therefore, when the administrative boundary changes in county level, the
boundary of zones should be revised accordingly. This dataset clarifies the
interrelationships among the various zones and components of each zone in
China, and reveals the regional differences of agricultural development status,
as well as resource and environmental issues in China. On one hand, from the
perspective of sustainably utilizing resources and the environment, the dataset
identifies the main constraints in each zone which can provide guidance for the
development direction, layout, and construction pathway of China??s differentiated
agricultural production. On the other hand, from the perspective of national
territory spatial utilization and layout, the dataset displays the spatial
distribution and regional differences of the agricultural resource suitability
and production potential in China. This provides a basis for formulating
agricultural production development strategies, and proposes ways to realize
the optimal allocation and improvement of agricultural resources and environment
in the various agricultural zones, ultimately assisting in practical decision-making.
Acknowledgements
Thanks
to Academician Shi, Y. L. for his valuable guidance and careful advice of the
zoning strategy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors
declare no conflicts of interest.
References
[1]
Shi, Y. L., Tang, H. L., Gao,
Z. Q., et al. Research on Key
Strategic Issues of Agricultural Resource and Environment in China [M].
Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2019.
[2]
Xu, E. Q. Dataset of
agricultural resource and environment zoning of China [J/DB/OL]. Digital Journal of Global Change Data
Repository, 2021. https://doi.org/10.3974/geodb.2021.02.07.V1.
[3]
GCdataPR Editorial Office.
GCdataPR Data Sharing Policy [OL]. https://doi.org/10.3974/dp.policy.2014.05 (Updated
2017).
[4]
Physical Regional Working
Committee of Chinese Academy of Sciences. Comprehensive Physical Regionalization
of China (Preliminary Draft) [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1959.
[5]
Agricultural Regional Planning
Group in National Agricultural Regional Committee of China. China Agriculture
Zoning [M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Press, 1981.
[6]
Shi, Y. L. Atlas of China??s
Land Resources [M]. Beijing: China Land Press, 2006.
[7]
China Vegetation Map Editorial
Committee, Chinese Academy of Sciences. 1:1 million Vegetation Map of People??s
Republic of China [M]. Beijing: Geology Press, 2007.
[8]
Li, B. Y., Li, J. Z. China??s
1:4 Million Geomorphic Map [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1994.
[9]
Ministry of Environmental
Protection of the People??s Republic of China and Chinese Academy of Sciences. National
ecological function zoning [R]. 2008.