Polychlorinated Biphenyls Dataset from
Multimedia Samples from Fildes Peninsula
and Xiehe Peninsula, Antarctica
Ge, L. K.1* Wang, Y. J.1 Gao, H.1 Zhang, P.1 Zhang, J.2 Li, R. J.1 Lu, Z. H.1 Liu, X.1 Na, G. S.1
1. Key Laboratory for Ecological Environment in Coastal Areas, State Oceanic Administration (SOA), National Marine Environmental Monitoring Center, Dalian 116023, China;
2. Polar Research Institute of China, Shanghai 200136, China
Abstract: Based on polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) data collection from samples in the multi-environmental media in vicinity of the Chinese Great Wall Station and Zhongshan Station at Fildes Peninsula and Xiehe Peninsula, Antarctica, we developed the Polychlorinated Biphenyls Dataset in the Multimedia Samples from Fildes Peninsula and Xiehe Peninsula, Antarctica (short name as “AntarcticPCBLevels"). It is the concentrations of 27 PCB congenersin 123 samples including air, seawater, snow, lake water and sediments, soils, penguin faeces, plants and intertidal benthos. Compared with the previous studies, this study provides more baseline data on PCBs occurrence in the Antarctic, which can support a comprehensive understanding of PCB long-range transport and polar distribution.
Keywords: Polychlorinated biphenyls; the Antarctic; Fildes Peninsula; Xiehe Peninsula; Multi environment tal-media
1 Introduction
Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) are toxic and bioaccumulative compounds that contaminate nearly all environmental matrices worldwide and are known to undergo global fractionation, accumulating toward the poles in a cold-trapping process[1–3]. Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are a class of ubiquitous POPs, which were used historically in electrical transformers and capacitors. Their persistence coupled with their potential toxicity has prompted international regulations and increased effort to understand their regional and global scale presence, especially in the Polar Regions. The occurrence of PCBs in the multi-environment of many countries and even in the Arctic is well documented[4–6]. However, limited data on PCBs have been reported in the Antarctic due to the difficulty of access.
Antarctica is concerned as an important sink for global POPs and is one of the most significant and sensitive areas in response to the global climate and environment changes. Thus, it is a significant research region for assessing persistence and long-range atmospheric transport of POPs, such as PCBs. In recent years, levels of PCBs have been found in the Antarctic air[7–9], snow [1] and fish [10] from southeast Antarctica. Baek, et al.[7] monitored atmospheric PCBs in Polar Regions and found a prevalence of lighter PCB congeners at the King George Island, Antarctica. Li, et al.[8–9] also found a very low air concentrations of PCBs that were dominated by tetra-PCBs, tri-PCBs and di-PCBs close to Chinese Great Wall Station, King George Island. These results indicated that the Polar area was contaminated with PCBs, which was mainly influenced by LRAT. Even so, the levels and distribution of PCBs are not well known in other multi-environmental media, such as snow, soil, seawater, sediments and marine organisms. Furthermore, multimedia occurrence of PCBs needs to be clarified in other Polar
areas, such as Xiehe Peninsula of the southwest Antarctica.
The present study reported levels of 27 PCB congeners in the multi-environmental media near the Chinese Great Wall Station and Zhongshan Station, which are located respectively at Fildes Peninsula and Xiehe Peninsula, Antarctica[11]. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report on the PCB concentrations in Antarctic multiple and comprehensive samples.
2 Metadata of Dataset
The metadata of “AntarcticPCBLevels” dataset is summarized in Table 1. It includes the dataset full name, short name, authors, year of the dataset, temporal-spatial resolution, data format, data size, data files, data publisher, and data sharing policy.
Table 1 Summary of the AntarcticPCBLevels metadata
|
Items
|
Description
|
|
Dataset full name
|
Polychlorinated biphenyls dataset from multimedia samples from Fildes Peninsula and Xiehe Peninsula, Antarctica
|
|
Dataset short name
|
AntarcticPCBLevels
|
|
Authors
|
Ge, L. K. A-3185-2017, Key Laboratory for Ecological Environment in Coastal Areas (SOA), National Marine Environmental Monitoring Center, lkge@nmemc.org.cn
Wang, Y. J. A-4111-2017, Key Laboratory for Ecological Environment in Coastal Areas (SOA), National Marine Environmental Monitoring Center, yjwang@nmemc.org.cn
Gao, H. A-3207-2017, Key Laboratory for Ecological Environment in Coastal Areas (SOA), National Marine Environmental Monitoring Center, hgao@nmemc.org.cn
Zhang, P. A-4102-2017, Key Laboratory for Ecological Environment in Coastal Areas (SOA), National Marine Environmental Monitoring Center, pzhang@nmemc.org.cn
Zhang, J. L-4784-2016, Polar Research Institute of China, zhangjie@pric.org.cn
Li, R. J. A-3183-2017, Key Laboratory for Ecological Environment in Coastal Areas (SOA), National Marine Environmental Monitoring Center, liruijing158@163.com
Lu, Z. H. K-8964-2015, Key Laboratory for Ecological Environment in Coastal Areas (SOA), National Marine Environmental Monitoring Center, luzihao1990209@outlook.com
Liu, X. A-3578-2017, Key Laboratory for Ecological Environment in Coastal Areas (SOA), National Marine Environmental Monitoring Center, xliu@nmemc.org.cn
Na, G. S. A-3185-2017, Key Laboratory for Ecological Environment in Coastal Areas (SOA), National Marine Environmental Monitoring Center, gsna@nmemc.org.cn
|
|
Geographic region
|
Fildes Peninsula (62°9¢30″S-62°13¢50″S, 59°0¢53″W-58°54¢6″W) and
Xiehe Peninsula (69°22′11″S- 69°24′33″S, 76°15′54″E-76°23′51″E), Antarctica
|
|
Year
|
2013-2014 Spatial resolution 1 km
|
|
(To be continued on the next page)
|
|
(Continued)
|
|
Items
|
Description
|
|
Data format
|
.xlsx
|
|
Data size
|
93 KB
|
|
Data files
|
2
|
|
Foundation(s)
|
National Natural Science Foundation of China (21377032); State Oceanic Administration of P. R. China (CHINARE 2014-02-01, 2014-03-04, 2014-04-01, 2014-04-03, 20120320, 201105013, KP201208)
|
|
Data publisher
|
Global Change Research Data Publishing & Repository, http://www.geodoi.ac.cn
|
|
Address
|
No. 11A, Datun Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing 100101, China
|
|
Data sharing policy
|
Data from the Global Change Research Data Publishing & Repository includes metadata, datasets (data products), and publications (in this case, in the Journal of Global Change Data & Discovery). Data sharing policy includes: (1) Data are openly available and can be free downloaded via the Internet; (2) End users are encouraged to use Data subject to citation; (3) Users, who are by definition also value-added service providers, are welcome to redistribute Data subject to written permission from the GCdataPR Editorial Office and the issuance of a Data redistribution license; and (4) If Data are used to compile new datasets, the ‘ten per cent principal’ should be followed such that Data records utilized should not surpass 10% of the new dataset contents, while sources should be clearly noted in suitable places in the new dataset[12]
|
3 Methods
3.1 Study Area
In the period of December 2013 to March 2014, the samples of air, seawater, snow, lake water and sediments, soils, penguin faeces, plants and intertidal benthos were collected from vicinity of the Chinese Great Wall Station and Zhongshan Station, which are located respectively at Fildes Peninsula and Xiehe Peninsula, Antarctica.
3.2 Data Collection or Processing
|
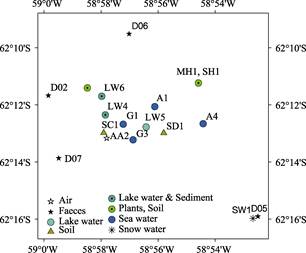
Figure 1 The location map of the samples near
the Fildes Peninsula, Antarctica
|
The dataset processing method referred to the article of “Distribution and transfer pattern of Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) among the selected environmental media of Ny-Alesund, the Arctic: As a case study” published in the journal Marine Pollution Bulletin [4]. The methods were described briefly as below.
Figure 1 shows the location map of the samples near the Fildes Peninsula, Antarctica. An active high-volume air sampler with glass fiber filters (GFF) and PUF disks was applied to capture particle-bound PCBs and gaseous PCBs from the atmosphere. PCBs in water samples were collected by C18 membranes and GFFs. An accelerated solvent extraction instrument (ASE350, Dionex, US) was applied to extract PCBs from the solid samples, including soils, sediments, plants and faces. The air and water samples were treated using an ultrasonic assistant extraction method. The condensed sulfur acid was used to remove the co-eluting interferences from the extract samples. After cleanup, the extracts were concentrated, spiked with internal standards and analyzed by Chromatography equipped with an Electric Capture Detector (GC-ECD, Agilent 7890A, US) and a tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS, Agilent 7000B, US).
4 Results and Validation
4.1 Dataset Product
The AntarcticPCBLevels dataset is comprised of two excel files, which correspond to the multimedia PCB concentrations of Fildes Peninsula and Xiehe Peninsula, respectively. The first File “Levels of polychlorinated biphenyls at Fildes Peninsula of Antarctica.xlsx” covers the levels of 27 PCB congeners in 42 samples of 12 environmental media from the region. The second File “Levels of polychlorinated biphenyls at Xiehe Peninsula of Antarctica.xlsx” includes the PCB levels in 81 samples of 10 environmental media. The minimum, maximum and mean concentrations of total PCBs (∑PCBs) were summarized in Table 2.
Table 2 Sample numbers (n) and concentration levels of ∑PCBs at Fildes Peninsula and Xiehe Peninsula
|
Media (unit)
|
Fildes Peninsula
|
|
Xiehe Peninsula
|
|
n
|
min
|
max
|
mean
|
|
n
|
min
|
max
|
mean
|
|
Air vapor (pg/m3)
|
8
|
3.85
|
16.11
|
10.13
|
|
13
|
2.50
|
38.12
|
11.69
|
|
Aerosol (pg/m3)
|
8
|
0.80
|
3.12
|
1.82
|
|
13
|
0.53
|
7.13
|
2.52
|
|
Seawater phase (ng/L)
|
4
|
0.26
|
0.58
|
0.38
|
|
–
|
–
|
–
|
–
|
|
Seawater particles (ng/L)
|
4
|
0.27
|
1.47
|
0.69
|
|
–
|
–
|
–
|
–
|
|
Snow water phase (ng/L)
|
1
|
–
|
–
|
0.47
|
|
6
|
0.27
|
0.38
|
0.33
|
|
Snow particles (ng/L)
|
1
|
–
|
–
|
0.29
|
|
6
|
0.08
|
0.78
|
0.34
|
|
Lake water phase (ng/L)
|
2
|
0.43
|
0.95
|
0.69
|
|
9
|
0.17
|
0.69
|
0.32
|
|
Lake water particles (ng/L)
|
2
|
0.62
|
1.03
|
0.83
|
|
9
|
0.18
|
0.70
|
0.42
|
|
Lake sediments (ng/g dw)
|
2
|
4.20
|
5.64
|
4.92
|
|
3
|
2.02
|
2.86
|
2.39
|
|
Soils (ng/g dw)
|
4
|
6.78
|
9.13
|
8.10
|
|
10
|
1.12
|
2.63
|
1.66
|
|
Faeces (ng/g dw)
|
7
|
10.08
|
60.03
|
27.02
|
|
–
|
–
|
–
|
–
|
|
Plants (ng/g dw)
|
2
|
13.05
|
15.23
|
14.14
|
|
10
|
2.46
|
11.10
|
5.37
|
|
Intertidal benthos (ng/g dw)
|
–
|
–
|
–
|
–
|
|
2
|
28.31
|
45.84
|
37.08
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.2 Data Validation
All sampling and analytical procedures were monitored using strict quality assurance and control measures[4]. For all samples, a method blanks, a matrix spike, a matrix spike duplicate, a sample duplicate and the field samples were analyzed as a batch. The PCB congeners were quantified with ECD and then confirmed with MS/MS. The concentrations of target compounds were quantified using internal standard method and corrected by the recoveries of PCB209, serving as surrogate standard. The recoveries of PCB209 in samples referred to Zhang, P., et al.[4]
5 Discussion and Conclusion
The AntarcticPCBLevels dataset covers comprehensive data of PCB concentrations in Antarctic multiple samples from Fildes Peninsula and Xiehe Peninsula, Antarctica. PCBs were detected ubiquitously in the Antarctic air, water, sediment, soil, faeces, plant and intertidal benthos. Compared with that in previous studies, this dataset can provide comprehensive assessment of PCB distribution and transfer pattern in the selected multi-environmental media.
Author Contributions
Na, G. S. designed the study. Ge, L. K. wrote the paper. Wang, Y. J., et al. contributed to the data processing, analysis and validation.
References
[1] Vecchiato, M., Argiriadis, E., Zambon, S., et al. Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) in Antarctica: Occurrence in continental and coastal surface snow [J]. Microchemical Journal, 2015, 119: 75-82.
[2] Ma, X. D., Zhang, H. J., Zhou, H. Q., et al. Occurrence and gas/particle partitioning of short- and medium-chain chlorinated paraffins in the atmosphere of Fildes Peninsula of Antarctica [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2014, 90: 10-15.
[3] Wang, Z., Na, G. S., Ma, X. D., et al. Occurrence and gas/particle partitioning of PAHs in the atmosphere from the North Pacific to the Arctic Ocean [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2013, 77: 640-646.
[4] Zhang, P., Ge, L. K., Gao, H., et al. Distribution and transfer pattern of Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) among the selected environmental media of Ny-Ålesund, the Arctic: as a case study [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2014, 89(1/2): 267-275.
[5] Mahmood, A., Syed, J. H., Malik, R. N., et al. Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in air, soil, and cereal crops along the two tributaries of River Chenab, Pakistan: Concentrations, distribution, and screening level risk assessment [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 481: 596-604.
[6] Zhang, R., Zhang, F., Zhang, T., et al. Historical sediment record and distribution of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in sediments from tidal flats of Haizhou Bay, China [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2014, 89(1): 487-493.
[7] Baek, S. Y., Choi, S. D., Chang, Y. S. Three-year atmospheric monitoring of organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in polar regions and the South Pacific [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2011, 45(10): 4475-4482.
[8] Li, Y., Geng, D., Hu, Y., et al. Levels and distribution of polychlorinated biphenyls in the atmosphere close to Chinese Great Wall Station, Antarctica: Results from XAD-resin passive air sampling [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2012, 57(13): 1499-1503.
[9] Li, Y. M., Geng, D. W., Liu, F. B., et al. Study of PCBs and PBDEs in King George Island, Antarctica, using PUF passive air Sampling [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2012, 51: 140-145.
[10] Lana, N. B., Berton, P., Covaci, A., et al. Fingerprint of persistent organic pollutants in tissues of Antarctic notothenioid fish [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 499: 89-98.
[11] Ge, L. K., Wang, Y. J., Gao, H., et al. Polychlorinated biphenyls dataset from multimedia samples from Fildes Peninsula and Xiehe Peninsula, Antarctica [DB/OL]. Global Change Research Data Publishing & Repository, 2014. DOI:10.3974/geodb.2014.02.11.V1.
[12] GCdataPR Editorial Office. GCdataPR Data Sharing Policy [OL]. DOI:10.3974/dp.policy.2014.05 (Updated 2017).