Remote
Sensing Image Based Wenshan Panax
notoginseng (GI) Distribution Dataset (2022)
Shen, J. P.1 Li,
Q.1
Wang, Y. Q.1* Liu, C.2 Yu,
B. H.2
1. China Land Surveying and Planning Institute,
Beijing100035, China;
2. Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural
Resources Research, Beijing100101, China
Abstract: Panax
notoginseng is a
commonly used and precious Chinese medicinal herb in China, It is also a
geographical indication product of Yunnan. High spatial resolution remote
sensing satellite data are used for the rapid monitoring of planting position
and scope of Panax notoginseng, and the scientific and
rational utilization of cultivated land resources, adjustment of diversified
agricultural structure, and the sustainable development of Panax notoginseng industry are
of great importance. The Panax
notoginseng planting dataset in Wenshan
Zhuang and Miao Autonomous Prefecture, Yunnan (2022), was developed using multisource
satellite images, including Pleiades, Gaofen series, ZY series and Beijing-2, and
a comprehensive mapping method, combined with arable land and garden
information in land survey data, field survey data, and historical data from
the ??Land Survey Cloud?? platform. Results show that the planting area of
Wenshan Panax notoginseng in 2022 was
approximately 8,295.75 ha. Spatially, the planting area decreased from
southwest to northeast. The dataset was archived in shapefile format and
consisted of eight data files with a total size of 8.25 MB (compressed to one
4.54 MB file).
Keywords: Wenshan,Yunnan; remote sensing image; Panax
notoginseng; geographical indication,2022
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3974/geodp.2024.01.07
CSTR: https://cstr.escience.org.cn/CSTR:20146.14.2024.01.07
Dataset Availability Statement:
The dataset supporting this paper
was published and is accessible through the Digital Journal of Global Change Data Repository
at: https://doi.org/10.3974/geodb.2024.05.02.V1
or https://cstr.escience.org.cn/CSTR:20146.11.2024.05.02.V1.
1 Introduction
Panax notoginseng is a plant of the Panax
genus in the Araliaceae family. It is a rare Chinese medicinal material in
China[1]. The growth of Panax notoginseng has specific climate and
altitude requirements, it also has higher requirements to the environmental, it
likes cool. In the first three years of Panax notoginseng??s growth, 8%–12%, 12%–15%,
and 15%–20% of light transmittance are needed[2-3]. Wenshan Zhuang
and Miao Autonomous Prefecture (hereinafter referred to as ??Wenshan Prefecture??) of Yunnan Province is the origin and main production area of Panax Notoginseng planting in China[4]; it has the
reputation of being ??the hometown of Panax notoginseng in China??. Panax notoginseng is not only a local characteristic
biological resource but also a pillar industry. However,
Panax notoginseng has strict
land requirements and cannot be continuously
cultivated, and soil for planting Panax notoginseng generally requires more than 10 years for replanting[5]. In recent years, the Panax
notoginseng industrial cluster has developed
quickly in Wenshan Prefecture, Panax
notoginseng planting occupies a large amount of cropland, cropland for Panax notoginseng cultivation are
gradually decreasing. The ??nongrain?? tendency caused by the cultivation of Panax notoginseng in Wenshan Prefecture has intensified, and the grain production and
demand remains tight balance. The Central
Committee of the Communist Party of China attaches great importance to food
security. In November 2020, the No. 44 (2020) of the General Office of the
State Council of the People??s Republic of China[6]
clearly stressed the need for the scientific and
rational use of cultivated land resources, studies on the relationship between
food production and economic benefits, and strict implementation of cultivated
land protection systems. Therefore, the monitoring of
planting location and scope of Panax notoginseng is of great practical importance
for the protection of cultivated lands, scientific and rational utilization of
cultivated land resources, food security, and supervision of functional areas for
food production.
The traditional monitoring of Panax
notoginseng cultivation mainly relies on census
statistics and on-site visits, which are time-consuming, laborious, and inefficient
and hardly objectively and truthfully reflect the actual planting situation in a
region on a macroscale. Panax notoginseng has strict light
transmittance requirements. Yunnan has good sunshine and solar radiation
conditions, in order to create an ideal growing environment, light
transmittance is often reduced by laying black sunshade nets[7,8]. Therefore, the spectral
characteristics of the plot planted in Panax
notoginseng are obviously different from those of other
surrounding ground objects, and this is the basis for monitoring Panax notoginseng planting through remote
sensing[9–13]. Chinese remote sensing
satellites enter the ??era of high resolution??, and domestic meter-level
satellite images have surged, image quality has considerably improved, and
satellites have the advantages, such as large coverage areas and short revisit
periods an so on; thus, remote sensing has become essential to crop planting
distribution and farmland rapid monitoring[14–17]. To date, the extraction
of planting information of Panax notoginseng mainly relies on data sources, such as 16m Gaofen-1[11],
10m Sentinel-2[4], 30m Landsat series, and TM/OLI[10], and
accurate monitoring studies and remote sensing images with spatial resolution
at the meter and submeter levels are lacking. The Ministry
of Natural Resources has deployed the Third National Land Survey, land change
investigations, and daily change investigations which is independently
conducted by local governments. These work have basically achieved survey
and monitoring at the meter and submeter levels in most areas of the country. However, the monitoring of cultivated and garden land at the
national scale is only segmented to secondary classification, and no clear
requirements have been made for planting crops. From
the protection of cultivated land and prevention of the ??nongrain?? phenomenon,
high-precision Panax notoginseng planting information is
needed as a important decision-making basis for the formulation of agricultural
production structure adjustment, making optimization policies, and supervision
measures for functional grain production areas. Remote sensing monitoring of Panax notoginseng planting provides a reference for the advanced exploration of
detailed monitoring of agricultural lands, such as cultivated and garden lands.
This study is mainly based on multisource domestic meter-level
satellite images combined with the location and scope of cultivated land and
gardens in the land survey data. Visual interpretation was used for the development
of the 2022 Panax notoginseng planting dataset in Wenshan Prefecture, Yunnan Province, and the
data were verified using ground survey and based the ??Land Survey Cloud??
platform internet + survey means. The aim is to provide
accurate samples and verification data for the intelligent remote sensing
monitoring of Panax notoginseng and basic data for food
security assessment, locate Panax notoginseng
planting areas, and contribute to relevant policy formulation in the Wenshan
area of Yunnan Province.
2 Metadata of the Dataset
The metadata of the dataset[18] is
summarized in Table 1.
Table 1 Metadata summary
of the dataset for comprehensive mapping of geographical indication product
planting area in cloudy and rainy areas of Southern China using multisource
satellite images: a case study of Panax notoginseng planting in Wenshan,
Yunnan (2022)
|
Items
|
Description
|
|
Dataset full name
|
Dataset for
comprehensive mapping of geographical indication product planting area in
cloudy and rainy areas of Southern China using multisource satellite images:
a case study of Panax notoginseng planting in Wenshan, Yunnan (2022)
|
|
Dataset short
name
|
Wenshan_SanQi_2022
|
|
Authors
|
Shen, J. P.,
China Land Surveying and Planning Institute, shenjp2023@163.com
Li , Q., China
Land Surveying and Planning Institute, 24640953@qq.com
Wang, Y. Q.,
China Land Surveying and Planning Institute, wangyq.14b@igsnrr.ac.cn
Liu, C.,
Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research,
lchuang@igsnrr.ac.cn
Yu, B. H.,
Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research,
yubh@igsnrr.ac.cn
|
|
Geographical region
|
Wenshan Zhuang
and Miao Autonomous Prefecture, Yunnan Province: 22??40ˊN–24??48ˊN, 103??35ˊE–106??12ˊE
|
|
Year
|
2022
|
|
Data format
|
.shp
|
|
|
|
Data size
|
8.25 MB
|
|
|
|
Data files
|
8 data files,
named in wenshan_sanqi_202.shp format
|
|
Foundation
|
Ministry of
Science and Technology of P. R. China (2021YFE0117300-4)
|
|
Data publisher
|
Global Change Research Data Publishing & Repository,
http://www.geodoi.ac.cn
|
|
Address
|
No. 11A, Datun
Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing 100101, China
|
|
Data sharing
policy
|
(1) Data are openly available and can be free
downloaded via the Internet; (2) End users are encouraged to use Data subject to citation; (3) Users,
who are by definition also value-added service providers, are welcome to
redistribute Data subject to
written permission from the GCdataPR Editorial Office and the issuance of a Data redistribution license; and (4) If
Data are used to compile new
datasets, the ??ten per cent principal?? should be followed such that Data records utilized should not
surpass 10% of the new dataset contents, while sources should be clearly
noted in suitable places in the new dataset[19]
|
|
Communication and searchable system
|
DOI, CSTR, Crossref, DCI, CSCD, CNKI,
SciEngine, WDS/ISC, GEOSS
|
3 Data Processing Methods
3.1 Study Area
Wenshan
Prefecture is located southeast of Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau (22??40ˊN–24??48ˊN, 103??35ˊE–106??12ˊE). Its
east-west transverse distance is 255 km2, its north-south
longitudinal distance is 190 km2, and its total area is 31,500 km2. Wenshan Prefecture has jurisdiction over one city and seven
counties, namely Wenshan City and Yanshan, Xichou, Malipo, Maguan, Qiubei,
Guangnan, and Funing Counties. In Wenshan Prefecture, the terrain is mainly
mountainous and decreases from northwest to southeast, and the altitude is
1,000–1,800 m. It has a subtropical climate, and precipitation is higher
than 1,000 mm but with an uneven distribution. Precipitation is more
frequent in the southwest than in the northeast, central, and western regions. The
average annual temperature is approximately 17.8??, showing the characteristics
of high temperatures in winter and weak high temperatures in summer[20].
Owing to the large relief of the terrain, the local microclimate characteristics are obvious.
According to the classification of land use status in 2022, the total area of
cultivated lands in Wenshan Prefecture is approximately 610,206 ha, and
the total area of garden lands is approximately 104,957 ha[21].
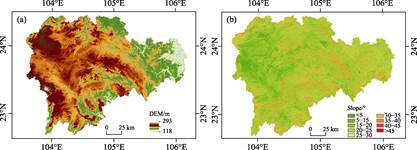
Figure 1 Topography (a) and landform (b) maps of
Wenshan Prefecture
|
Figure 2 Remote sensing image base map of
Wenshan Prefecture in 2022
|
3.2 Data Source and Pre-processing
All the data used in this
dataset are domestic remote sensing satellite images with high spatial
resolutions within 2 m, the image collection period is from September to
November 2022. The sensor types mainly include the French Pleiades, domestic
Jilin-1, Gaofen-7, ZY-3, ZY-1, Beijing-2,
Gaofen-1, Gaofen-2, and Gaofen-6 (Figure 2 and Table 2). More than 70% of the area had 0.5 m
resolution image data; 29.4%, 1-m resolution; and 0.14%, 2-m resolution, which
are mainly used to fill the cloud coverage area, the specific situation is shown in Table 2. The acquired remote sensing images have geometric distortions because
of the sensors, surface topography, and other factors. The original images must
be pre-processed mainly through geometric precision correction, image
enhancement fusion, and image registration. In
addition, land-type statistical data on land use status classification
Table 2 Data source of
satellite images
|
No.
|
Data source
|
Original
image resolution captured
|
Image
resolution after fusion
|
Area (km2)
|
|
1
|
Jilin-1
|
Panchromatic:
0.5
m; Multispectral: 2 m
|
0.5
m
|
10,742.25
|
|
2
|
Jilin-1
|
Panchromatic:
0.75 m; Multispectral: 3 m
|
1
m
|
7,671.72
|
|
3
|
Pleiades
|
Panchromatic:
0.5 m; Multispectral: 2 m
|
0.5
m
|
11,400.56
|
|
4
|
Gaofen-7
|
Panchromatic:
0.8 m; Multispectral: 3.2 m
|
1
m
|
1350.04
|
|
5
|
Gaofen-2
|
Panchromatic:
0.8 m; Multispectral: 3.2 m
|
1
m
|
165.94
|
|
6
|
Beijing-2
|
Panchromatic:
0.8 m; Multispectral: 3.2 m
|
1
m
|
37.85
|
|
7
|
Gaofen-1
|
Panchromatic:
2 m; Multispectral: 8 m
|
2
m
|
38.23
|
|
8
|
ZY-3
|
Panchromatic:
2.1 m; Multispectral: 5.8 m
|
2
m
|
4.07
|
|
9
|
ZY-1
|
Panchromatic:
2.5 m; Multispectral: 10 m
|
2
m
|
0.69
|
|
10
|
Gaofen-6
|
Panchromatic:
2 m; Multispectral: 8 m
|
2
m
|
0.31
|
in
Wenshan Prefecture and counties (cities) of Yunnan Province in 2022 were
collected, including garden plots, cultivated lands, and dry lands and so on[21],
and auxiliary information, including terrain and geomorphology data, was used as
reference for interpreting Panax notoginseng planting area.
3.3 Interpretive Flag
Establishment
Remote
sensing interpretation is based on information, such as spectral feature
difference, size, shape, and texture of ground objects. Panax notoginseng is a shade-loving plant and needs to be covered by a shade shed during
its growing period. Shade sheds used to control light transmittance are mainly
black plastic sunshade nets, which are the physical basis for extracting the
planting area of Panax
notoginseng through remote sensing. For large-scale
remote sensing, information about target ground objects is obtained through comprehensive
mapping. This study is based on field data and experience obtained from field
investigations, and field evidence photos provided by the ??Land Survey Cloud??
platform, using multisource high-resolution remote sensing data for the
analysis of the color, texture, and other features of the planting area of Panax notoginseng. Ultimately, the remote sensing interpretation markers of Panax notoginseng planting were established (Table 3).
Table 3 Interpretive signs
of Panax
notoginsengin Wenshan Prefecture
|
Region
|
Longitude
(E)
|
Latitude
(N)
|
Image
|
Photo
|
Region
|
Longitude
(E)
|
Latitude
(N)
|
Image
|
Photo
|
|
Wenshan City
|
103.938,5??
|
23.651,3??
|

|

|
Maguan County
|
104.361,6??
|
22.933,0??
|

|

|
|
103.866,3??
|
23.562,7??
|

|

|
Qiubei County
|
103.861,1??
|
24.102,2??
|

|

|
|
Yanshan County
|
104.176,2??
|
23.838,3??
|

|

|
|
103.853,4??
|
23.893,2??
|

|

|
|
104.176,2??
|
23.864,8??
|

|

|
Guangnan County
|
104.736,0??
|
24.018,8??
|

|

|
|
Xichou County
|
104.795,3??
|
23.583,0??
|

|

|
Funing County
|
105.380,6??
|
23.382,7??
|

|

|
|
Malipo County
|
104.575,6??
|
23.150,8??
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
3.4 Indoor Interpretation
Compared
with machine learning, manual visual interpretation has the advantages of high
flexibility, strong interpretation, and wide applicability. To prevent the
influences of water bodies and mountain shadows on the remote sensing
monitoring of Panax notoginseng planting, this
study adopts the comprehensive mapping method to accurately interpret the
planting situation of Panax notoginseng in
Wenshan Prefecture. First, this study created a spatial location consistency
database to initially define the planting area of Panax notoginseng, integrating multisource remote sensing image data, cultivated land
and garden information of land change survey, digital elevation models, and
climatic data. Then, the color features, texture structure,
and shape features of the remote sensing images were used in the extraction of
the suspected planting plots of Panax notoginseng through manual visual interpretation in the ArcGIS platform. According
to the interpretation results, the actual planting situation of Panax notoginseng was
verified using field investigation data, and the preliminary interpretation
results were adjusted and optimized for the accurate delineation of the
specific boundaries of Panax notoginseng planting areas.
4 Data Results
and Validation
4.1
Data Composition
The Dataset consists
of one shapefile. The dataset is the planting data of Panax notoginseng in Wenshan Prefecture in 2022 and stored in .shp format, including eight
data files with a total size of 8.25 MB (compressed into 4.54 MB,
named Wenshan_SanQi_2022 form).
4.2 Data Results
In
2022, the planting data of Panax notoginseng in
Wenshan Prefecture were collected using a
total of 15,405 planting plots with a planting area of about 8,295.75 ha (Table
4), which is extremely close to the planting area announced by Wenshan Prefecture
in 2022 (125,400 mu=8,360 ha). As
shown in Table 4, the Panax notoginseng planting among these counties,
Wenshan City is the largest and has the largest planting area, accounting for nearly
one-third of the whole prefecture, followed by Yanshan, Qiubei, and Maguan
Counties, which all have a planting area of more than 1,000 ha. The above counties accounted for more
than 85% of the planting area of Panax notoginseng in
Wenshan Prefecture. By contrast, Xichou, Malipo, Guangnan, and Funing Counties
had small Panax notoginseng planting areas,
accounting for less than 15%. From the perspective of
spatial distribution, the planting area of Panax notoginseng in Wenshan Prefecture is
mainly distributed in the southwest, decreasing from southwest to northeast (Figure 3). In terms of topography and geomorphology, Panax notoginseng planting areas are mostly distributed in areas above 1,000 m,
and a few plots in Xichou, Malipo, Machan, Guangnan, and Funing Counties are
distributed below 1,000 m. The slope of Panax notoginseng is mainly
distributed between 10?? and 15?? (Table 5). From the
perspective of concentration, the planting center of Panax notoginseng in Wenshan Prefecture was located in an oval area of approximately
12 km ?? 10 km in the southeast, and the hot spots are mainly located
in Wenshan City, Qiubei County, and Yanshan County.
Table 4 Remote sensing monitoring
statistics of Panax notoginseng planting in each county (city) of
Wenshan Prefecture
|
Administrative division code
|
Administrative division name
|
Number of planting
plots (piece)
|
Planting area
(ha)
|
Ratio (%)
|
|
532601
|
Wenshan City
|
3,384
|
2,552.99
|
30.77%
|
|
532622
|
Yanshan County
|
2,159
|
1,561.52
|
18.82%
|
|
532623
|
Xichou County
|
646
|
281.92
|
3.40%
|
|
532624
|
Malipo County
|
832
|
336.97
|
4.06%
|
|
532625
|
Maguan County
|
4,837
|
1,437.83
|
17.33%
|
|
532626
|
Qiubei County
|
2,205
|
1,517.89
|
18.30%
|
|
532627
|
Guangnan County
|
1,043
|
478.96
|
5.77%
|
|
532628
|
Funing County
|
299
|
127.67
|
1.54%
|
|
Total
|
Wenshan
Prefecture
|
15,405
|
8,295.75
|
100%
|
|
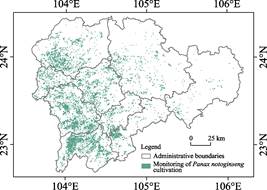
Figure 3 Spatial distribution of Panax
notoginseng plants in Wenshan Prefecture in 2022
|
According
to the classification data of land use status in 2022, the
cultivated land in Wenshan prefecture is 610,206 ha, of which dry land
cover 504,604 ha, accounting for
82.69%;
the garden land area in Wenshan prefecture is 104,957 ha, of which other
gardens
land cover 55,840 ha, accounting for 53.20%. According to the work
classification of the Third National Land Survey, the fields where perennial crops, such as medicinal materials, are
planted are included in the ??other garden land??
category. Therefore, approximately 14.86% of the ??other garden land?? areas in the state are Panax notoginseng
planting areas. More
than half of the ??other garden land?? areas in Wenshan City cultivate Panax notoginseng, accounting for 56.23%; nearly
one-third of the ??other garden land?? area in Qiubei, Yanshan, Malipo, and
Maguan Counties cultivate Panax notoginseng.
From the perspective of the proportion of Panax notoginseng planting area in the dry land area, that is, the
proportion of cultivated ??nongrain?? land caused by the cultivation of Panax
notoginseng, the results show that Wenshan City and Maguan County accounted
for a relatively high proportion (3.22% and 3.34%, respectively); Yanshan, Xichou, and Qiubei Counties accounted for 1.41%,
1.38%, and 1.34% respectively,
and Guangnan and Funing Counties
accounted for 0.62% and 0.41% respectively (Table 6).
Table 5 Topography and landform of Panax
notoginseng planting in each county (city) of Wenshan Prefecture
|
Administrative division name
|
Altitude (m)
|
Slope (??)
|
|
Minimum
|
Maximum
|
Average
|
Minimum
|
Maximum
|
Average
|
|
Wenshan
City
|
1,131
|
2,228
|
1,696
|
0.0
|
52.3
|
12.2
|
|
Yanshan
County
|
1,216
|
2,183
|
1,560
|
0.0
|
49.2
|
11.1
|
|
Xichou
County
|
865
|
1,723
|
1,462
|
0.0
|
44.9
|
14.7
|
|
Malipo
County
|
375
|
1,858
|
1,262
|
0.0
|
45.8
|
14.6
|
|
Maguan
County
|
195
|
2,043
|
1,614
|
0.0
|
54.3
|
13.9
|
|
Qiubei
County
|
1,217
|
2,408
|
1,771
|
0.0
|
42.6
|
10.8
|
|
Guangnan
County
|
782
|
1,819
|
1,452
|
0.0
|
42.1
|
12.4
|
|
Funing
County
|
229
|
1,614
|
925
|
0.3
|
32.8
|
7.9
|
Table 6 Proportion of Panax notoginseng planting in
cultivated land and garden land in each county (city) of Wenshan Prefecture
|
Administrative division name
|
The proportion of occupied garden land (%)
|
The proportion of occupied other garden land
(%)
|
The proportion of occupied arable land
(%)
|
The proportion of occupied dry land
(%)
|
|
Wenshan City
|
32.99
|
56.23
|
2.85
|
3.22
|
|
Yanshan County
|
19.80
|
32.06
|
1.21
|
1.41
|
|
Xichou County
|
6.64
|
10.88
|
1.09
|
1.38
|
|
Malipo County
|
5.33
|
33.07
|
0.97
|
1.13
|
|
Maguan County
|
12.94
|
30.09
|
2.65
|
3.34
|
|
Qiubei County
|
20.34
|
28.14
|
1.23
|
1.34
|
|
Guangnan County
|
1.40
|
5.38
|
0.45
|
0.62
|
|
Funing County
|
0.49
|
0.54
|
0.29
|
0.41
|
|
Wenshan Prefecture
|
7.90
|
14.86
|
1.36
|
1.64
|
5 Discussion and Conclusion
5.1 Discussion
Panax notoginseng planting monitoring information in Wenshan Prefecture, Yunnan Province,
was obtained using multisource meter-level remote sensing satellite images and
topographic and geomorphic information in 2022. At a high spatial resolution,
the comprehensive mapping method was used for the identification of surface
crop types, exhibiting high reliability and effectiveness.
According to the obtained dataset, the spatial layout characteristics of Panax notoginseng planting
in Wenshan Prefecture were discussed, and the agglomeration rules and
differences in Panax notoginseng planting in terms of geographical distribution, landform, and other
factors were revealed. Combined with the main data results of the classification of land
use status in 2022, through the comparative analysis of planting land of Panax notoginseng and grain planting land, the influence of planting Panax notoginseng in Wenshan Prefecture on the ??nongrain?? local cultivated land was
estimated. The results can provide data for the formulation
of policies balancing economic development and cultivated land protection,
implementation of agricultural structure adjustment, and sustainable
development of characteristic medicinal materials.
5.2 Conclusion
On the
basis of remote sensing satellite images with high spatial resolution (mainly
0.5 and 1 m) in 2022, this study developed a dataset of Panax notoginseng sample points in Wenshan Zhuang and Miao Autonomous Prefecture of
Yunnan Province (2022) through comprehensive mapping and field investigation.
The results are highly consistent with the planting area data published on the
official website of Wenshan Prefecture. The spatial distribution of Panax notoginseng planting areas in Wenshan Prefecture was analyzed, and the contribution
of Panax notoginseng planting to the ??nongrain??
cultivated land in Wenshan Prefecture was preliminarily estimated using main
data results of land use classification in 2022. The main conclusions are as
follows:
(1) Based
on multisource high spatial resolution remote sensing data, such as Jilin-1,
Gaofen Series, ZY series, Beijing-2, and French Pleiades, the location and
scope of Panax notoginseng planting plots were accurately identified by visual interpretation
and multivariate features, such as spectral information and texture
information, provided strong data support for the spatial distribution
monitoring of Panax notoginseng planting areas.
(2) The planting area of Panax notoginseng in Wenshan Prefecture is approximately 8295.75 ha. Wenshan
City is the largest producing area, accounting for nearly one-third of the
whole prefecture, followed by Yanshan, Qiubei, and Maguan Counties. They
accounted for more than 85% of the planting area of Panax notoginseng in the whole prefecture. The planting area is mostly distributed in
the area of more than 1,000 m, and the slope is mainly concentrated
between 10?? and 15??.
(3) Panax notoginseng planting is an
important factor in the ??nongrain??
cultivated land in Wenshan Prefecture. In terms of ??nongrain??
conversion caused by garden lands, the contribution rate of Panax notoginseng planting
in Wenshan Prefecture is 7.9%. From the perspective of cultivated land
occupation, the ??nongrain?? contribution rate caused by the cultivation of Panax notoginseng planting
in Wenshan City and Maguan County is relatively high, accounting for approximately
3%.
Author
Contributions
Wang, Y. Q. gave general
guidance to the research and development of the dataset and revised the data
paper; Shen, J. P. sorted out the remote sensing image dataset and auxiliary
data, interpreted Panax notoginseng planting data, analyzed the related results, and wrote the data
paper; Li, Q. inspected the planting plots of Panax notoginseng and verified relevant
datasets; Liu, C. and Yu, B. H. revised the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
[1]
Cui, X. M., Lei, S. W.
Standardized Planting Technology of Panax notoginseng [M]. Kunming:
Yunnan Science and Technology Press, 2015.
[2] Meng, X. X., Huang, L. F., Dong L. L., et al. Analysis of global ecology of
Panax notoginseng in suitability and quality [J]. Acta Pharmaceutica
Sinica, 2016, 51(9): 1483–1493.
[3] Yang, W. C., Zhu, Y. Y., Zhang, R. K., et al. Studies on the engineering
and technical system of integrating agricultural machinery and agronomic based
on sustainable development of Panax notoginseng industry [J]. Hubei
Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 53(1): 122–125+129.
[4]
Li,
Y. C., Zhang, J., Zhang, P., et al. Study on area of Panax notoginseng in Wenshan
Prefecture of Yunnan Province based on Sentinel-2 [J]. Journal
of Yunnan University: Natural Sciences Edition, 2022, 44(1): 89–97.
[5] Sun, X. T., Li, L., Long, G. Q., et
al. The progress and prospect on consecutive monoculture problems of Panax
notoginseng [J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2015, 34(3): 885–893.
[6] General Office of the State Council of the People's Republic of
China. Opinions on Preventing the "Non-grain Conversion" of
Cultivated Land and Stabilizing Grain Production of the General Office of the State Council [EB/OL]. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2020-11/17/content_5562053.htm.
2020-11-04.
[7] Cui, X. M., Wang, C. L., He, C. F., et al. Preliminary study on the transmittance of Panax
notoginseng shade [J]. Journal of Chinese
Medicinal Materials, 1993, 16(3): 3–6.
[8] Liu, S. L. Construction techniques for planting greenhouses of Panax
notoginseng in central Yunnan [J]. Biotech
World, 2014(12): 54+56.
[9] Zhang, X. B., Sun, Y. Z., Huang, L. Q., et al. Establish remote of sensing
monitoring method and standard on wild rare medical plant [J]. China Journal
of Chinese Materia Medica, 2009, 34(13): 1741–1744.
[10] Wu, F. Z., Zheng, M. H., Hu, W. Y., et al. Remote sensing extraction and
change analysis of Panax notoginseng planting area in Wenshan Prefecture
of Yunnan Province in past decade based on TM and OLI data [J]. Acta
Agriculturae Jiangxi, 2021, 33(6): 90–97.
[11] Zhu, Z., Yuan, X. P., Gan, S., et
al. GF-1 remote sensing data for Panax notoginseng planting
information extraction in Wenshan, Yunnan Province [J]. Journal of Zhejiang
A & F University,
2020, 37(1): 129-135.
[12] Shi, T. T., Zhang, X. B., Guo, L. P., et al. Study on extraction method of Panax notoginseng plots
in Wenshan of Yunnan province based on decision tree model
[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2017, 42(22): 4358–4361.
[13] Dai, C. X., Xie, X. J., Xu, Z. G., et al. Monitoring and analyzing herbal medicine plantation via
remote sensing: a case study of pseudo-ginseng in Wenshan and Honghe Prefecture
of Yunnan Province [J]. Remote Sensing for Land and Resources, 2018, 30(1): 210–216??
[14] Qu, R., Nie, Y. H., Zhang, Y. Q., et al. Study on extraction of
plasticulture basing on GF-1 of high resolution image of China [J]. Environment
and Sustainable Development, 2018, 43(6): 66–69.
[15] Gao, W. Research on extraction of ginseng planting area based on
remote sensing image [D]. Beijing:
Beijing Jiaotong University, 2022.
[16] Cai, Z. W., He, Z., Wang, W. J., et
al. Mapping cropland at metric resolution using the spatiotemporal
information from multi-source GF satellite data [J]. National
Remote Sensing Bulletin, 2022, 26(7): 1368–1382.
[17]
Yang,
J., Chu, Q. F., Luo, J. S., et al. Study on the extraction method of crop planting
structure based on the results of geographical conditions [J]. Geomatics & Spatial Information Technology,
2020, 43(S1): 29–34.
[18] Shen, J. P., Li, Q., Wang,Y. Q., et
al. Dataset for comprehensive mapping of geographical indication product
planting area in cloudy and rainy areas of Southern China using multisource
satellite images: a case study of Panax notoginseng Planting in Wenshan,
Yunnan (2022) [J/DB/OL]. Digital Journal of Global Change Data Repository,
2024. https://doi.org/10.3974/geodb.2024.05.02.V1.
[19] GCdataPR Editorial Office. GCdataPR data sharing policy [OL].
https://doi.org/10.3974/dp.policy.2014.05 (Updated 2017).
[20] Wenshan Prefecture Bureau of Statistics. 2023 Wenshan Statistical
Yearbook [EB/OL]. https://www. ynws.gov.cn/info/5726/314534.htm. 2023-11-22.
[21] Land Survey Results Sharing Application Platform.Summary Table of
Land Use Status Classification Area [OL]. https://gtdc.mnr.gov.cn/Share#/thirdSurvey.
2024-05-20.