Photosynthetically Active Radiation (PAR) Dataset at 5 km Spatial Resolution over China-ASEAN (2013)
Zhang, H. L Xin, X. Z.* Li, L. Yu, S. S. Li, X. J. Zhong, B. Liu, Q. H.*
State Key Laboratory of Remote Sensing Science, Institute of Remote Sensing and Digital Earth, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China
Abstract: Photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) is a key parameter for ecosystem modeling and climate change. PAR data for China and the Association of Southeast Asian Nations were derived from geostationary and polar-orbiting images with 5 km spatial resolution and daily temporal resolution. These data were stored in an HDF5 file. Data from each day were stored as one single file for the year 2013. The input for this dataset was from MTSAT-2, a stationary satellite belonging to the Japan Meteorological Agency, with a temporal resolution of one hour, and the surface albedo product was derived from MODIS products with 16-day resolution. The algorithm for the dataset used a lookup table (LUT) method based on the radiative transfer model, and the instantaneous PAR was derived from the LUT based on cloud mask. The daily PAR was calculated from the hourly instantaneous PAR. Quality control and quality checking were performed prior to release of the dataset.
Keywords: China; Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN); Photosynthetically Active Radiation (PAR); 5 km
1 Introduction
Photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) is an important parameter for ecosystem and land surface models[1]. A PAR dataset for China-ASEAN with 5 km spatial resolution[2] was constructed using China-ASEAN regional remote sensing and monitoring research data. This also represents an important dataset for regional environmental monitoring in China-ASEAN with spatial and temporal resolution. This dataset was based on data from stationary satellite MTSAT-2 and polar-orbiting satellite MODIS. Using the radiative transfer model, a lookup table (LUT) was first created and PAR data for clear and cloudy skies were then derived.
2 Metadata of Dataset
The descriptions of the China-ASEAN PAR dataset (MuSyQ-PAR-5km-2013) are recorded here (Table 1). This information includes the dataset full name, dataset short name, authors, geographical region of the dataset content, year of dataset, dataset spatial and temporal resolution, dataset format and size, data publisher, data sharing platform and contact information, foundation, the data sharing policy and so on.
Table 1 Summary of the China-ASEAN PAR metadata
|
Items
|
Description
|
|
Dataset full name
|
Dataset of photosynthetically active radiation (5 km and daily) 2013 in China-ASEAN
|
|
Dataset short name
|
MuSyQ-PAR-5 km-2013
|
|
Authors
|
Zhang, H. L. L-6168-2016, Institute of Remote Sensing and Digital Earth, Chinese Academy of Sciences, zhanghl@radi.ac.cn
Xin, X. Z. S-3681-2016, Institute of Remote Sensing and Digital Earth, Chinese Academy of Sciences, xin_xzh@163.com
Li, L. S-4533-2016, Remote Sensing and Digital Earth, Chinese Academy of Sciences, lili3982@163.com
Yu, S. H. S-4050-2016, Institute of Remote Sensing and Digital Earth, Chinese Academy of Sciences, yushan0427@163.com
Zhong, B. L-4528-2016, Institute of Remote Sensing and Digital Earth, Chinese Academy of Sciences, zhongbo@radi.ac.cn
Liu, Q. H. S-1647-2016, Institute of Remote Sensing and Digital Earth, Chinese Academy of Sciences, liuqh@radi.ac.cn
|
|
Geographical region
|
10°55′12″S–53°32′24″N, 73°37′12″E–141°0′36″E
The region covers the area of the following 11 nations: Brunei, Cambodia, China, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam
|
|
Year
|
2013; Temporal resolution: daily
|
|
Spatial resolution
|
5 km; Number of files: 365; Data format: .hdf; Data size: 340 MB
|
|
|
Data files
|
The dataset of each day was archived as one single HDF file and named DataSet_PAR, which represents daily photosynthetically active radiation
|
|
|
Foundation(s)
|
Ministry of Science and Technology of P. R. China (2012AA12A304, 2012AA12A305, 2013AA12A301)
|
|
Data publisher
|
Global Change Research Data Publishing and Repository, http://www.geodoi.ac.cn
|
|
Address
|
No. 11A, Datun Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing 100101, China
|
|
Data sharing policy
|
Data from the Global Change Research Data Publishing & Repository includes metadata, datasets (data products), and publications (in this case, in the Journal of Global Change Data & Discovery). Data sharing policy includes: (1) Data are openly available and can be free downloaded via the Internet; (2) End users are encouraged to use Data subject to citation; (3) Users, who are by definition also value-added service providers, are welcome to redistribute Data subject to written permission from the GCdataPR Editorial Office and the issuance of a Data redistribution license; and (4) If Data are used to compile new datasets, the ‘ten per cent principal’ should be followed such that Data records utilized should not surpass 10% of the new dataset contents, while sources should be clearly noted in suitable places in the new dataset[3]
|
3 Methodology
The PAR inversion method has been published[4]. The general technical procedure for the 5 km PAR was as follows: cloudy/clear sky pixels were distinguished first, and cloud optical thickness (COT) was inverted for cloudy sky, while the aerosol optical depth (AOD) and total precipitation water were inverted for clear sky. Based on the atmospheric radiative transfer model, two LUTs containing various atmospheric conditions and PAR were created for clear sky and cloudy sky. The instantaneous PAR was interpolated from the LUT, and the daily PAR was calculated from the instantaneous PAR with hourly temporal resolution. The overall process for the PAR dataset is shown in Figure 1.
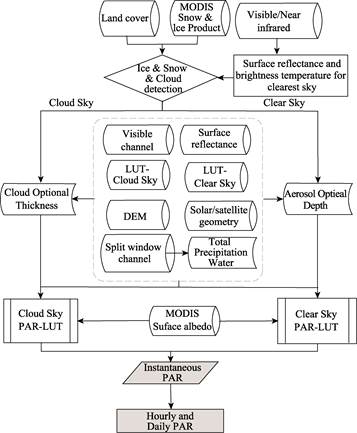
Figure 1 The generation process for the 5 km PAR dataset
Firstly, cloud detection was implemented to distinguish between clear sky and cloudy sky, adopting the cloud depiction and forecast system (CDFS) model to perform the cloud analysis[5]. Cloud recognition was realized by three steps: (1) temporal difference, (2) dynamic threshold, and (3) spectrum recognition. Each of these steps utilizes different characteristics of clouds in terms of time, space, and spectrum to efficiently and correctly analyze clouds. Total precipitation water and AOD were inverted for clear sky while COT was inverted for cloudy sky. The inversion method has been previously described[6].
Using the LUT created from the radiative transfer model and taking the atmospheric parameter created by the inversion of stationary satellite data as the input, a rough estimate of instantaneous PAR was achieved by the interpolation of the LUT. The temporal resolution of the stationary satellite was one hour; so, the hourly and daily PAR can be calculated by totaling the hourly instantaneous PAR.
4 Dataset Composition
The spatial resolution of the China-ASEAN PAR dataset is 5 km, and the temporal resolution is one day. The HDF5 storage format was adopted for the dataset. The Dataset for each day was archived into a single file, and it was composed of two parts: metadata information and the data product. The metadata information comprises projection type and parameters, units, scale factor, offset, range of valid values, and filling values. The data entity was named “Daily_PAR” and contains the daily PAR values. The size of each data file is about 9 MB. The distribution of PAR in 2013 is shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2 Distribution of PAR in China-ASEAN in 2013
5 Verification of Data Reliability
Measurements of solar radiation from Chinese solar radiation stations were used to validate daily PAR. The PAR conversion factors and solar radiation vary for different seasons, vegetation types, and phenology of vegetation; most conversion factors are in the range of 0.44-0.50[3–4]. In this study, the mean conversion factor was 0.47. However, apart from the data corresponding to the China region, the remaining data covering the ASEAN region still require verification.
In east, central, northeast, and north China, the MBE values between the total daily PAR estimated by the model and the measured values were in the range of 5.02-8.27 W/m2, with a root-mean-square error (RMSE) of between 25.89 W/m2 and 17.13 W/m2 and an R2 of above 0.86. The MBE in southwest China was 9.60 W/m2 with an RMSE of 19.36 W/m2. However, in the southwest mountainous area (Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau, Sichuan, Chongqing, and other areas), the estimated values were lower than the measured values due to the impact of terrain. Furthermore, for the Tibetan Plateau, because of its special terrain and atmospheric characteristics, the MBE between the analog value of PAR and the measured value was 2.02 W/m2, with an RMSE of 20.92 W/m2 and an R2 of 0.75.
6 Conclusion
The data reported here are comparatively high in reliability and spatial resolution, and diverse in temporal resolution. The data can be used as the primary input data for regional ecological and environmental change assessments, climate models, hydrological models, and vegetation growth change analysis.
Author Contributions
Zhang, H. L. and Xin, X. Z. developed the methodology for PAR. Li, L. performed the PAR dataset validation. Yu, S. S. developed the algorithm for cloud detection. Zhong, B. and Liu, Q. H. designed and quality controlled by Zhong, B. and Liu, Q. H.; Zhang, H. L. and
Liu, Q. H. completed the data paper.
References
[1] Alados, I., Foyo-Moreno, I., Olmo, F. J., et al. Improved estimation of diffuse photosynthetically active radiation using two spectral models [J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2002, 111(1): 1-12. DOI: 10.1016/s0168-1923(02)00046-1.
[2] Zhang, H. L., Xin, X. Z., Li, L., et al. Dataset of Photosynthetically Active Radiation (5 km and daily) 2013 in China-ASEAN [DB/OL]. Global Change Research Data Publishing & Repository, 2015. DOI: 10.3974/geodb.2015.02.05.V1.
[3] GCdataPR Editorial Office. GCdataPR data sharing policy [OL]. DOI: 10.3974/dp.policy.2014.05 (Updated 2017).
[4] Li, L., Xin, X. Z., Zhang, H. L., et al. A method for estimating hourly photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) in China by combining geostationary and polar-orbiting satellite data [J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2015, 165: 14-26. DOI: 10.1016/j.rse.2015.03.034.
[5] Moon, P. Proposed standard solar radiation curves or engineering use [J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 1940, 230(5): 583-618. DOI: 10.1016/S0016-0032(40)90364-7.
[6] McCree, K. J. A solarimeter for measuring photosynthetically active radiation [J]. Agricultural Meteorology, 1966, 3(5/6): 353-366. DOI: 10.1016/0002-1571(66)90017-3.