Global Change Data Encyclopedia
Caka Salt Lake, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China
Gou, Z. J. Liu, F. G.*
Department of Geographic Sciences, Qinghai Normal University, Xining 810008, China
Keywords: Caka Salt Lake; Qinghai-Tibet Plateau; Qinghai province; salt lake; data encyclopedia
|

Figure 1 The geo-location of Caka Salt Lake (Google Earth)
|
Caka Salt Lake is located in Wulan county, Qinghai province, P. R. China. Caka means “salt lake” in Mongolian and Tibetan languages, also known as Dabuson Nur. It is located in the eastern Qaidam basin on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, 56 km west of Qinghai Lake and 47 km east of Dulan Lake. Its geo-location is 36°38′5″N-36°45′34″N, 98°59′43″E-99°12′25″E (Figure 1, Figure 2). Caka Salt Lake has an elevation of 3,100 m above sea level, an area of 139.39 km2 (2015) and the coastline of 74.27 km (2015)[1–2].
Caka Salt Lake is located on the continental fault zone between the mountains of Nanshan Mountain and Ela Mountain in Qinghai province. The mountains around the lake basin are Paleozoic strata. The basin is distributed widely by Quaternary eluvium, including alluvial gravels and Aeolian dunes, lacustrine sandy clay, halite, gypsum and other chemical deposits. In the early Late Pleistocene, Caka Salt Lake and Gonghe basin were located in the same basin. At that time, the lake had not developed yet[3]. The Mohe River and Gaowei River flowing into Caka Salt Lake were the upper reaches of the Shazhuyu River in Gonghe basin, flowing from west to east into the Yellow River. Then due to the changes in basement structure and the influence of environmental aridity, the river’s shear force on uplift structure weakened. In the late Pleistocene, the Shazhuyu River evolved into two independent water systems, of which Gaowei River flowed back west into the Caka basin, forming a closed inland lake and gradually evolved into the current pattern. The lake is shaped like an ellipse, with Wanyan Tongbu Mountain in the north, Wangxiu Mountain in the south and Chatang basin in the east[4].
|
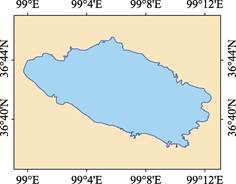
Figure 2 Geographic information data map of Caka Salt Lake (.shp format)
|
The lake, in a semi-arid desert region, has annual precipitation about 200 mm and evaporation about 2,000 mm. The water is mainly supplied by surface runoff and spring water gushing from catchment areas. There are more than 80 springs in the lake region. The surface runoffs flowing into the lake region are short intermittent streams, of which Gaowei River and Mohe River are the longest rivers in the basin. Salt crystals are called “green salt” because they contain minerals and thus are bluish black. The lake is rich in minerals and contains more than 40 kinds of brine chemical composition, which is an important treasure for Chinese inorganic salt industry. The density of the lake water is 1.218, the pH value is 6.8, and the salinity is 322.49 g/L, belonging to magnesium sulfate subtype salt lake[3]. Caka Salt Lake has a long history of development. With the development of tourism, it is reputed as “the mirror of the sky” and is also called “the four great sights of Qinghai” together with Tar Temple, Qinghai Lake, and Mengda Tianchi Lake[5].
The Caka Salt Lake dataset consists of 15 data files, which are archived in .shp[6] and .kmz[7] data formats. The data size is 337 KB (compressed in 2 data files, 137 KB).
References
[1] Gou, Z. J., Liu, F. G. Caka Salt Lake [DB/OL]. Global Change Research Data Publishing & Repository, 2018. DOI: 10.3974/geodb.2018.04.14.V1.
[2] Xi’an Surveying and Mapping General Station, Starmap Press. Map of Qinghai Province [M]. Beijing: Starmap Press, 1999.
[3] Editorial Office of Encyclopedia of Rivers and Lakes in China. Encyclopedia of Rivers and Lakes in China: Section of River Basins in Southwest Region [M]. Beijing: China Water & Power Press, 2014.
[4] Editorial Office of National Geographic Series. Top Places to Go Around China [M]. Blue Sky Publishing House, 2012.
[5] https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1594161229784435768.
Data Computing Environment
[6] ESRI. ArcGIS campus license of Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
[7] Google LLC. Google Earth Pro. 7.3.2.5481 (32-bit), hk.google.com.
URL for Data Downloading
http://www.geodoi.ac.cn/WebEn/doi.aspx?ID=925.
Or search through: http://www.geodoi.ac.cn.