GIES Case Dataset on Yucheng
Wheat-grain Double Cropping Yellow River
Irrigation Farmland in Fangsi Town, Shandong Province of China
Wang, Z. B.1* Li, K. X.1 Huang, Y. H.1 Lyu, J. L.2 Zhou, L.3 Chen, X.4 Li, T.4 Wen D. H.5 Ni, W. T.5 Shao, Y.6 Zhu, X. G.7 Liu, J.4 Shao, J.4 Chen, L. J.4
1.Institute of Geographic Sciences and
Natural Resources Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China;
2. Institute of Wheat Research, Dezhou
Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Dezhou 253000, China;
3. Yucheng Municipal Government, Yucheng
251200, China;
4. Yucheng Municipal Bureau of
Agricultural and Rural Affaires, Yucheng 251200, China;
5. Yucheng Fangsi Local Government,
Yucheng 251200, China;
6. Yucheng Maixiangyuan Food Co., Ltd., Yucheng
251200, China;
7. Beijing Tianhang Create Co., Ltd., Beijing
100085, China
Abstract: Yucheng city is located in the
alluvial plain of Yellow River in the northwest of Shandong province with a
long history in agriculture and is the place where legendary Da Yu tamed the
floods. Yucheng is also of the pilot zone for the showcase of saline-alkali
soil improvement by the Chinese Academy of Sciences. The case area of Fangsi
Town, Yucheng, is located at 37??N, which is moist but not wet in
summer and dry but not parch in winter. The unique natural conditions and
advanced cultivation make the case area an ideal place for quality special
wheat and high starch maize. Wheat-maize double cropping is the characteristic
agricultural mode of Yucheng Fangsi. This study collected the data of physical
geography, crop varieties, management, and agricultural history of the case
area, analyzed the geographical genes of agricultural products, and explored
the relationship between environmental protection and sustainable development,
so as to provide informed support for the effective link between the ecology
and Rural Revitalization in Yucheng. The dataset includes: (1) GIS boundary
data of Fangsi town and Yucheng city; (2) physical geographical data, including
climate, soil, water and NDVI; (3) quality data of wheat and maize; (4)
cultivation data of wheat and maize; (5) standard and quality of wheat
processed products; (6) management data of processed wheat products; (7) in
situ photos. The dataset is archived in .shp, .xls, .jpg, .pdf and .docx
formats with a size of 48.1 MB (45.9 MB in compression).
Keywords: Yucheng; Fangsi town; Yellow River irrigation area; wheat-maize double
cropping; GIES Case 9
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3974/geodp.2021.04.05
CSTR: https://cstr.escience.org.cn/CSTR:20146.14.2021.04.05
Dataset Availability Statement:
The dataset
supporting this paper was published and is accessible through the Digital Journal of
Global Change Data Repository at: https://doi.org/10.3974/geodb.2021.12.44.V1 or
https://cstr.escience.org.cn/CSTR:20146.11.2021.12.44.V1.
1 Introduction
Yucheng city is
located in the alluvial plain of the Yellow River in the northwest of Shandong
province. Yucheng got its name from Dayu. According to legend, Dayu was one of
the earliest tribal leaders of the Chinese people and tamed the flood in
today??s Yucheng. It is also an area for Chinese scientists to demonstrate their
evolving technologies to treat poor soils on a large scale. Since the 1950s,
the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the Chinese Academy of Agricultural
Sciences have developed high-standard farmland in the entire area of Yucheng
through sand and alkali control, agricultural development, and water-saving
irrigation. Fangsi town of Yucheng is located at the golden zone nearby 37??N .
It is moist but not wet in summer and dry but not parch in winter. Therefore, it has superior conditions for twice
cropping of winter wheat and summer maize. Double cropping of wheat and grain
is the typical cropping mode of Fangsi in Yucheng. This study comparatively
analyzes the multiple datasets of physical geography, crop varieties, cultivation
management, and history of the Yucheng wheat-grain double-ripening Fangsi
irrigation area, and explores the collaborative relationship between
environmental protection and sustainable development in the case area, aiming
to provide a feasible case for the compelling connection between ecological
civilization construction and rural revitalization in Yucheng.
2 Metadata of the
Dataset
The metadata of the Wheat-maize double
cropping field in Yellow River Irrigation Fangsi Town case dataset on
environment protection and sustainable development[1] is summarized in Table 1. It includes the dataset full
name, short name, authors, year of the dataset, temporal resolution, spatial
resolution, data format, data size, data files, data publisher, and data
sharing policy, etc.
3 Geographical
Scope of the Case Area
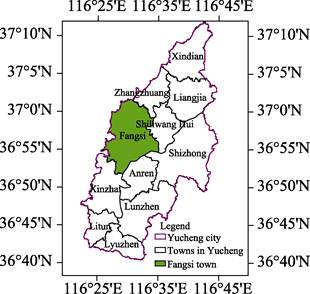
The case study area
is located at Fangsi town. Fangsi is a town under the jurisdiction of Yucheng,
Dezhou city (prefecture), Shandong province, with an area of 146.24 km2.
Fangsi town has 11 communities and 123 administrative villages. The geographical scope is the farmland of
wheat-maize in Fangsi town, with a total area of 63.96 km2
(Figure 1, 2).
4 Ecological and
Geographical Environment
The case area is
located in the alluvial plain in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow
River, which is classified as the warm temperate semi-humid monsoon climate
area and is a typical alluvial plain. The parent material for soil formation is
Yellow River alluvial and sediment. The soil surface texture is mostly medium
loam, and the soil layer is deep and easy to cultivate[3]. Soil pH
is generally neutral or slightly alkaline and rich in nutrients, such as
nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. The case area is a yellow-diversion
irrigation area located in the second largest irrigation sector in the lower
reaches of the Yellow River.
Table 1 Metadata
summary of Wheat-maize double cropping field in Yellow River Irrigation Fangsi
Town case dataset on environment protection and sustainable development[1]
|
Items
|
Description
|
|
|
Dataset full name
|
Wheat-maize double cropping
field in Yellow River Irrigation Fangsi Town case dataset on environment
protection and sustainable development
|
|
Dataset short name
|
YuchengWheatMaizeCase09
|
|
Authors
|
Wang, Z. B., Institute of
Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research (IGSNRR),
Chinese Academy of Sciences
(CAS), wangzb@igsnrr.ac.cn
Li, K. X., IGSNRR, CAS,
likx@igsnrr.ac.cn
Huang, Y. H., IGSNRR, CAS
Lyu, J. L., Institute of Wheat
Research, Dezhou Academy of Agricultural Sciences
Zhou, L., Yucheng Municipal
Government
Chen, X., Yucheng Municipal
Bureau of Agricultural and Rural Affaires
Li, T., Yucheng Municipal
Bureau of Agricultural and Rural Affaires
Wen, D. H., Fangsi town local
government, Yucheng
Ni, W. T., Fangsi town local
government , Yucheng
Shao, Y., Yucheng Maixiangyuan
Food Co., Ltd.
Zhu, X. G., Beijing Tianhang
Create Technology Co., Ltd.
Liu, J., Yucheng Municipal
Bureau of Agricultural and Rural Affaires
Shao, J., Yucheng Municipal
Bureau of Agricultural and Rural Affaires
Chen, L. J., Yucheng Municipal
Bureau of Agricultural and Rural Affaires
|
|
Geographical area
|
Fangsi, Yucheng city, Shandong
province
|
|
|
|
Year
|
1991-2021
|
|
|
|
Data format
|
.shp, .pdf, .xls, .docx, .jpg
|
|
|
|
|
Data size
|
48.1 MB
|
|
|
|
|
Data files
|
Case range, physical
geography, variety characteristics, operational management
|
|
Foundation
|
Chinese Academy of Science
Institution-Local Cooperation Project
|
|
Data
publisher
|
Global
Change Research Data Publishing & Repository, http://www.geodoi.ac.cn
|
|
Address
|
No.
11A, Datun Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing 100101, China
|
|
Data
sharing policy
|
Data from
the Global Change Research Data Publishing & Repository includes metadata, datasets
(in the Digital Journal of Global Change Data Repository), and
publications (in the Journal of Global Change Data & Discovery). Data sharing policy
includes: (1) Data are openly available and can be free downloaded via the
Internet; (2) End users are encouraged to use Data subject to
citation; (3) Users, who are by definition also value-added service
providers, are welcome to redistribute Data subject to written permission
from the GCdataPR Editorial Office and the issuance of a Data redistribution
license; and (4) If Data are used to compile new
datasets, the ??ten per cent principal?? should be followed such that Data
records utilized should not surpass 10% of the new dataset contents, while
sources should be clearly noted in suitable places in the new dataset[2]
|
|
Communication and searchable system
|
DOI,
CSTR, Crossref, DCI, CSCD, CNKI, SciEngine, WDS/ISC, GEOSS
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.1
Climatic Conditions
Yucheng
is in a warm-temperate semi-humid continental monsoon climate zone, where there
is plenty of heat and light, as well as simultaneous rain and heat, which makes
it ideal for agriculture. The average temperature in this region is 13.1 ??C,
and the average precipitation is about 567 mm (1,144.4 mm in wet years and 238 mm
in dry years).
Precipitation shows a clear seasonal
pattern with most precipitation occurring in summer (65 % of
the total per year), and less in the winter and spring (20 % of the total per
year)[4]. According to Fangsi town??s meteorological data for the
past 30 years (provided by Yucheng Meteorological Bureau), monthly
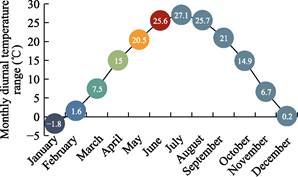
meteorological data for the past 30 years in the case area are shown in Figure 3-6.
During the wheat flowering and maturity period (April to June), the average
temperature in the case area over the past 30 years is 20.36 ??C, and the average daily temperature range is from 11.3 to
11.6 ??C. It is beneficial for wheat grains to improving the protein content as
well as to extending dough stability times[4],
which are favorable for the production of high-quality wheat.
|
|

|
|
Figure 1 Geographical location of
Fangsi town
|
Figure 2 Wheat-maize
region in Fangsi town
|
|

|
|
|
Figure 3 Monthly average sunshine hours
|
Figure 4 Monthly average temperature
|
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Figure 5 Monthly
precipitation
|
Figure 6 Monthly
diurnal temperature range
|
4.2 Soil
Physic-Chemical Properties
The
soil type of Fangsi town is brown soil, which is medium loam and sandy loam[3].
Soil samples from two layers were collected in this study. Cadmium (Cd),
chromium (Cr), nickel (Ni), lead (Pb), zinc (Zn), and copper (Cu) content (mg/kg),
and pH were measured by the Physicochemical Analysis Center of the Institute of
Geographic Sciences and Resources, Chinese Academy of Sciences. The soil
samples showed no detectable cadmium (Cd),
with the detection of chromium (Cr) in the range of 69.8 to 88.6 mg/kg, nickel
(Ni) in the range of 38.7 to 48.2 mg/kg, lead (Pb) in the range of 41.8 to 50.2
mg/kg, zinc (Zn) in the range of 32.2 to 63.0 mg/kg, and copper (Cu) in the range
of 22.6 to 25.9 mg/kg. The detection of pH
was near neutral and was good for soil microorganisms (Table 2). Sampling tests
revealed a good soil environment, and the heavy metal content is far lower than
the pollution risk screening value and risk control value designated by the National
agricultural soil standard.
Table 2 Soil pH and heavy metals of the case
area
|
Test items
|
Fangsi town
(0-10 cm)
|
Fangsi town
(10-20 cm)
|
Yucheng
(0-10 cm)
|
Yucheng
(10-20 cm)
|
GB15618??2018 National standard: arable
soil risk
|
|
Screening value
|
Control value
|
|
pH
|
6.7
|
6.9
|
6.9
|
6.9
|
|
|
|
Cd (mg/kg)
|
Undetected
|
Undetected
|
Undetected
|
Undetected
|
0.3
|
3.0
|
|
Cr (mg/kg)
|
88.6
|
72.9
|
70.1
|
69.8
|
200.0
|
1000.0
|
|
Ni (mg/kg)
|
48.2
|
42.1
|
38.9
|
38.7
|
100.0
|
|
|
Pb (mg/kg)
|
50.2
|
42.7
|
41.8
|
43.5
|
120.0
|
700.0
|
|
Zn (mg/kg)
|
32.2
|
63.0
|
35.8
|
36.5
|
250.0
|
|
|
Cu (mg/kg)
|
25.9
|
23.4
|
22.7
|
22.6
|
100.0
|
|
4.3 Water Quality
Surface water and groundwater samples were collected from
Fangsi town and its surrounding areas.
The chromium (Cr), manganese
(Mn), iron (Fe), nickel (Ni), copper (Cu), zinc (Zn), arsenic (As), cadmium
(Cd), and lead (Pb) concentration (mg/L) and pH for aqueous environment in the
case area were determined by the Physicochemical Analysis Center of Institute
of Geographic Sciences and Resources of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Table
3, 4). Samples showed that the pH of surface water and groundwater and the
content of heavy metals in Fangsi Town meet the National Class I standards of
surface water and groundwater.
Table 3 Statistics of surface
water quality of the case area
|
Test items
|
Fangsi town
|
Yucheng
|
GB3838??2002 National surface water standard
|
|
Class I
|
Class III
|
|
pH
|
6.6
|
6.6
|
6-9
|
6-9
|
|
Cr (mg/L)
|
0.000
|
0.000
|
0.01
|
0.05
|
|
Mn (mg/L)
|
0.001
|
0.023
|
0.1
|
0.1
|
|
Fe (mg/L)
|
0.001
|
0.007
|
0.3
|
0.3
|
|
Ni (mg/L)
|
0.002
|
0.001
|
0.02
|
0.02
|
|
Cu (mg/L)
|
0.002
|
0.001
|
0.01
|
1.0
|
|
Zn (mg/L)
|
0.000
|
0.001
|
0.05
|
1.0
|
|
As (mg/L)
|
0.008
|
0.009
|
0.02
|
0.05
|
|
Cd (mg/L)
|
0.000
|
0.000
|
0.001
|
0.005
|
|
Pb (mg/L)
|
0.000
|
0.000
|
0.01
|
0.05
|
5 Varieties and Quality
of Wheat and Maize
In the case area, the dominant
wheat varieties are Jimai 44 and Shiluan 02-1, and the leading
maize variety is Denghai 605. The
variety and quality data of wheat and maize are provided by Bureau of
Agricultural and Rural Affaires of Yucheng city[5].
5.1
Varieties of Wheat and Maize
Wheat: Jimai 44 (Figure 7).
Accession number is Lu Wheat 20180018.
This variety is winterness. The seedlings are semi creeping; the plant
type is semi compact; the leaf color is light green; the flag leaves rush up;
the lodging resistance is good and the ripening color is good. It has a long
awn, a white shell, a white grain, and a hard grain among other
characteristics.
Wheat: Shiluan 02-1
(Figure 8). Accession number is National
Wheat 2007016. This variety is semi-winterness. The
seedlings are creeping, with strong tillering ability and high panicle rate.
The plant type is compact; the leaf color is light green; the leaf is small and
lifted up, and the spike layer is tidy. The spike is spindle type, with short
villus, long awn, white shell, white grain, full grain and horny.
Maize: Denghai 605 (Figure 9). Accession number is National Maize 2010009. This variety is compact, with a plant height of 259 cm and a spike height of
99 cm. The spike is long tube type with 18 cm long; the number of rows per spike is 16-18 with rea axis; The grain is yellow and horse tooth shape, while
100 grains weigh 34.4 g.
Table 4 Statistics of groundwater quality in case area
|
Groundwater environment
|
Fangsi town
|
Yucheng
|
GBT14848-2017 National groundwater standard
|
|
|
Class I
|
Class III
|
Class IV
|
|
|
pH
|
6.6
|
6.4
|
6.5-8.5
|
6-9
|
6-9
|
|
|
Cr (mg/L)
|
0.000
|
0.000
|
0.005
|
0.05
|
0.1
|
|
|
Mn (mg/L)
|
0.000
|
0.383
|
0.050
|
0.1
|
1.5
|
|
|
Fe (mg/L)
|
0.000
|
0.002
|
0.100
|
0.3
|
2.0
|
|
|
Ni (mg/L)
|
0.000
|
0.000
|
0.002
|
0.02
|
0.1
|
|
|
Cu (mg/L)
|
0.000
|
0.001
|
0.010
|
1.0
|
1.5
|
|
|
Zn (mg/L)
|
0.000
|
0.001
|
0.050
|
1.0
|
5.0
|
|
|
As (mg/L)
|
0.001
|
0.004
|
0.001
|
0.01
|
0.05
|
|
|
Cd (mg/L)
|
0.000
|
0.000
|
0.000
|
0.005
|
0.01
|
|
|
Pb (mg/L)
|
0.000
|
0.000
|
0.005
|
0.00
|
0.1
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|

|
|
Figure 7 Wheat variety:
Jimai 44
|
Figure 8 Wheat variety: Shiluan 02-1
|
Figure 9 Maize variety: Denghai 605
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5.2 Quality
of Wheat and Maize
The wheat quality
data are shown in
Table 5. Jimai 44 has a grain bulk density of 788.9 g/L, a grain protein
content of 15.4% in grains, a wet gluten content of 35.1%, and a stabilization
time of 25.4 minutes. Shiluan 02-1
has a grain bulk density of 820 g/L, a protein content of 17%-18%
in grains, 41% in wet gluten and a stabilization time of more than 20 minutes.
Wheat quality of Fangsi
town exceeded National standard GB/T 17892??1999, achieving the first grade of
wheat and strong gluten wheat. In a horizontal comparison, it is evident that
Fangsi town produces superior wheat compared to those planted in other origins.
Pull-breaking force is significantly correlated with crude protein
content of wheat flour and stability time, which is the key index for the
sensory evaluation of cooked wheaten food[6]. The wheat varieties in
the case area have high protein content and long stabilization time, indicating that they have superior
characteristics.
The data of maize variety Denghai 605 in Fangsi town is shown in
Table 6. The grain bulk density of grain is 766 g/L, exceeding national maize
standard (Class I); the crude protein content is 9.35%, crude fat content is
3.76%, crude starch content is 73.40%, lysine content is 0.31%, which are
higher than that of maize products from other origins.
Table 5 Wheat quality
inspection in Fangsi Town
|
Varieties of wheat
|
Grain bulk density (g/L)
|
Grain protein
(%)
|
Wet gluten
(%)
|
Stabilization time (minutes)
|
|
Jimai 44
|
788.9
|
15.4
|
35.1
|
25.4
|
|
Shiluan 02-1
|
820
|
17-18
|
41
|
>20
|
|
GB/T 17892??1999 National standard high-quality wheat, strong
gluten wheat (Class I)
|
770
|
15
|
35
|
10
|
|
Shiluan 02-1 (Luancheng, Hebei province)[7]
|
777
|
14.34
|
31.80
|
12.9
|
|
Shiluan 02-1 (Mixed samples from Xingtai
and Handan, Hebei province, Anyang and Xinxiang, Henan province) [8]
|
787
|
12.91
|
31.80
|
22.0
|
Table 6 Quality comparison of
maize in Fangsi with national standards and maize in other parts of China[9]
|
Maize varieties
|
Grain bulk density
(g/L)
|
Crude protein
(%)
|
Crude fat
(%)
|
Crude starch
(%)
|
Lysine
(%)
|
|
Denghai 605
|
766
|
9.35
|
3.76
|
73.40
|
0.31%
|
|
National standard GB 1353??
2018 maize (First Category)
|
720
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shandong
|
739
|
9.8
|
4.2
|
71.1
|
-
|
|
Hebei
|
748
|
9.1
|
3.9
|
71.5
|
-
|
|
Shanxi
|
753
|
9.3
|
3.7
|
71.3
|
-
|
|
Inner Mongolia
|
745
|
8.8
|
4.1
|
71.5
|
-
|
|
Liaoning
|
756
|
9.2
|
4.2
|
71.4
|
-
|
|
Jilin
|
738
|
8.8
|
4.2
|
71.8
|
-
|
|
Heilongjiang
|
717
|
8.4
|
4.4
|
71.7
|
-
|
|
Henan
|
735
|
9.8
|
4.0
|
71.5
|
-
|
|
Shanxi
|
727
|
9.4
|
3.7
|
71.1
|
-
|
5.3 Wheat
Products
5.3.1 Wheat Product Standards
The wheat products in the present
case study include dumpling flour, steamed bread flour and whole wheat flour in
the ready mixed flour of pastry produced by Yucheng Maixiangyuan Food Co., Ltd. The followed
standards are: National standard for wheat flour (GB/T 1355??1986), Wheat flour
for shandong dumplings (T/SDAS 70??2019), Wheat flour for shandong steamed bread
(T/SDAS 71??2019), and Wheat flour for Shandong noodles (T/SDAs 72??2019).
5.3.2 Wheat Product Quality
Dumpling powder, steamed bread
flour and whole wheat flour produced by Yucheng Maixiangyuan Co., Ltd. have
obtained green food certification.
The nutrition test report of the pastry ready mixed powder shows that: The energy content is 1,523 kJ/100g; the
contents of protein, fat and carbohydrate are 24.4%, 1.7% and 61.5%
respectively.
6 Management
and Traditional Culture of Wheat and Maize in Yucheng
6.1
Management
6.1.1 Scientific and Standardized Planting
(1) Agricultural calendar of winter wheat-summer maize
planting model. The key periods of winter
wheat-summer maize system are listed in Table 7.
(2) Key measures to promote agriculture in case area are summarized as follows:
1) Promote agricultural industry through land
concentration and crop structure adjustment; 2) build a grain industry chain of
??institute + government + enterprise + cooperative + service center??; 3) establish
an industrial cluster of high-quality wheat along the Yellow River in Shandong;
4) uplift water use efficiency by using the agricultural decision support
system of the CAS; 5) extend quality varieties such as high gluten wheat and
quality maize, together with Shandong Seed Group; 6) Build the brand of ??37??N High-Quality Wheat??; 7) promote
whole-process land trusteeship services, together with Shandong Agricultural
Group. Once the Group signs a contract with farmers, it will uniformly provide
seed, farming, sowing, pest control, harvesting and other services; 8) Cultivate
precision agriculture, and optimize all elements of agriculture (soil, seeds,
machinery, etc.)
6.1.2 Long-term Habitat Observation
To better manage wheat and maize in
the case area, a billboard for the scope of the case area (Figure 10) and a
ground observation station (Figure 11) were set up in Fangsi town. The station is a low-power internet of things sensing
system, which can collect key crop growth environment factors all day: landscape,
meteorological elements, air quality, soil, water, crop growth, diseases and
pests.
Table 7 Agricultural calendar and main field management in case area
|
Crop
|
Month
|
Agricultural calendar
|
Field management measures
|
|
Wheat
|
Mid and late Sept.
|
Before sowing
|
Preparation of seed
and fertilizer
|
|
|
Early to mid Oct.
|
Wheat sowing
|
Sufficient
fertilizer and fine land treatment to ensure quality
|
|
|
Mid Oct.-mid Dec.
|
Before dormancy
|
Ensure full and even
seedlings before winter
|
|
|
March
|
Wheat rejuvenation
|
Tailored irrigation
and fertilization for various fields
|
|
|
April-May
|
Jointing to grouting
|
Irrigation and
fertilization, prevent diseases and insect pests
|
|
|
Late May-early
June
|
Wheat ripening
|
Timely harvest
|
|
Maize
|
Mid and late May
|
Before sowing
|
Preparation of seed
and fertilizer
|
|
|
Early to mid June
|
Maize sowing
|
Ensure full and even
seedlings
|
|
|
Mid June-early
July
|
Seedling
|
Ensure strong maize
seedlings
|
|
|
Early July-early Aug.
|
Jointing-heading
|
Remove weak plants,
apply fertilizer, prevent disease and lodging
|
|
|
Early Aug. -late Sept.
|
Heading-maturity
|
Irrigation and
fertilization, timely harvest
|
6.1.3 Long-Term Habitat Observation
To better manage wheat and maize
in the case area, a billboard for the scope of the case area (Figure 10) and a ground observation station
(Figure 11) were set up in Fangsi town. The station is a low-power internet of things sensing
system, which can collect key crop growth environment factors all day: landscape,
meteorological elements, air quality, soil, water, crop growth, diseases and
pests.
6.1.4 The Role of Agricultural Enterprises: Yucheng Maixiangyuan Food Co.,
Ltd.
The business of
Yucheng Maixiangyuan Food Co., Ltd. includes wheat planting, flour R &D,
pasta processing training, e-commerce, agricultural tourism, etc. It is the
first listed enterprise in China for steamed bread, a high standard whole chain
enterprise of Chinese staple food, a leading enterprise and standardized wheat planting
base in Shandong province. The company??s technologies, ??three-time-proofing,
three-time-rising, eight-time-noodle- pressing, low temperature proofing
production??, have obtained the national patent of new technologies.
Aided by Yucheng Agricultural Chamber of Commerce, Maixiangyuan improved
its links with local farmers, provided them with unified wheat seeds and
standardized field techniques, promoted the large-scale wheat cultivation and uplifted
the quality of wheat. Maixiangyuan also cooperated with the Chinese Academy of
Sciences to establish a brand staple grain R&D base to enhance the brand
value of wheat products.
|

|

|
|
Figure 10 Case area billboard
|
Figure 11 Observation station
|
6.2
History of Land Use
6.2.1 The History of Special
Wheat Cultivation
As
early as 2000, Shandong conducted the land zoning for special wheat and classified
Dezhou into the most suitable area for special wheat[10,11]. In 2009,
the national wheat zoning by the Ministry of Agriculture included five
high-quality wheat producing areas, of which Dezhou (Prefecture) is one of the
most suitable areas for high-quality strong gluten and medium gluten wheat. Dezhou further detailed the main production
areas of special wheat to county-level bases, such as Wucheng, Pingyuan, Qihe, and
Yucheng. Wheat is No.1 crop in Yucheng. Normally, the sowing area is 49,000 ha
and the yield is 395,000 tons. Yucheng was awarded the ??National Super Grain-Producing
County??[4]. Yucheng encourages high-quality wheat processing
industry. At present, there are large grain enterprises such as Yufei Flour,
Zhanyue Food and Dezhou Jinbo. In 2019, the Guidelines for Grain Industry and
Rural Revitalization was published.
6.2.2 Improvement of Saline-Alkali Soil in Yucheng
Before 1960, the
proportion of poor soil in Yucheng was as high as 43%, mainly saline and alkali
soil. Since the 1960s, scientists from the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), have
started the research on the improvement of saline alkali soil in the lower
reaches of the Yellow River, and set up research bases. By the late 1980s,
large scale (667 ha) saline alkali soil improvement demonstration fields had
been established.
Meanwhile, the research base in Yucheng was developed into
Yucheng Experimental Station of Chinese Academy of Sciences in 1979, run by the
Institute of Geography of Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). Over the past 40
years, based on the Station, CAS has developed a number of technical systems to
meet the needs in different agricultural stages. For example, ??Well Irrigation and
Well Drainage?? technology for salt and alkali soil improvement in 1960s; ??Well,
Ditch, Leveling, Fertilizer, and Forest?? technology for salt and alkali soil improvement
in the 1970s (wheat-maize double cropping is one of the key parts); Comprehensive
technology for severe saline-alkali and sandy soil improvement in 1980s; Efficient
planting and animal husbandry technology in the 1990s; comprehensive technology
for maize production and recycling industry in the 2000s[12].
Thanks to these saline and alkali soil improvement
technologies, the grain yield per unit area under the ??wheat-maize double cropping
system?? in Yucheng city has reached 15 ton /ha in 2021. In the future, with the
improvement of farmland infrastructure (ditch, bridge, road, canal, culvert,
well, forest and electricity), as well as the construction of the water source
project of Shinu lake and the clean-up and siltation project of Tuhai river,
the soil productivity of Yucheng will be further improved, and the maize yield
in the core area is expected to be 22.5 ton/ha.
7 Discussion
and Conclusion
Fangsi town of Yucheng, located in the alluvial plain of
the Yellow River, boasts suitable climate, soil and water resources for quality
winter wheat and summer maize double-cropping. Appropriate natural conditions,
combined with effective cultivation techniques, have nurtured high-quality
wheat and maize products with geographic characteristics. Through this case
study, the relevant data and knowledge have been collected, analyzed and published,
including the natural geographic data, variety data, management data, and
historical data. Based on this effort, we have provided useful ideas and
scientific and technological support for Yucheng to promote its rural
revitalization and the healthy development of modern agriculture.
Author Contributions
Wang,
Z. B. designed the study; Li, K. X. designed sampling and analysis of soil,
water and plants, wrote the manuscript; Huang, Y. H. took part in data
processing and manuscript writing; Lv, J. L. collected wheat data; Zhou, L.,
Chen, X., Li, T., Wen, D. H., and Ni, W. T. assisted data collection and logistics;
Shao, Y. collected corporate data; Zhu, X. G. installed observation station;
Liu, J., Shao, J., and Chen, L. J. participated in the data collection. Wang, Z.
B. and Zhou, L. finalized the paper.
Conflicts of
Interest
The
authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
[1]
Wang Z. B., Li K. X.,
Huang Y. H., et al. Wheat-maize
double cropping field in Yellow River Irrigation Fangsi Town case dataset on
environment protection and sustainable development [J/DB/OL]. Digital Journal of Global Change Data
Repository, 2021. https://doi.org/10.3974/geodb.2021.12.44.V1. https://cstr.escience.org.cn/CSTR:20146.11.2021.12.44.V1.
[2]
GCdataPR Editorial Office. GCdataPR data sharing policy [OL].
https://doi.org/10.3974/dp.policy.2014.05 (Updated 2017).
[3]
Liu, Z. H. Status and development strategy of high quality
special wheat industrialization in Yucheng [D]. Tai??an: Shandong Agricultural
University, 2014.
[4]
Wang, D., Yu, Z. W, Zhang, Y. L. Meteorological regionalization for
quality strong gluten and medium gluten wheat in Shandong Province [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,
2007(10): 2269?C2276.
[5]
Yucheng Agricultural and Rural Bureau.
Operating procedures for major agricultural varieties and technologies in
Yucheng City [R]. 2021.
[6]
Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of
the P. R. China. China wheat quality report in 2013[R]. 2013.
[7]
Jia, X. X., Cao, Y., Wang, S. B., et al. Quality analysis of
strong-gluten wheat and common wheat in some areas in 2016 [J]. Cereal and Feed Industry, 2017(8): 8?C15.
[8]
National Food and Strategic Reserves
Administration. Quality report newly harvested maize in 2019 [R]. 2019.
[9]
Liu, T. T., Zhang, W. J., Peng, J. Y., et al. Correlation analysis between
quality of high-quality strong- and medium-gluten wheat flour and noodle
properties in Huanghuai wheat area [J/OL]. Journal of
the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association: 1?C10 [2021-12-26].
http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2864.ts.20211203. 2258.005.html.
[10]
Wu, T. Q., Guo, H. H., Zhang, X. J., et al. Planting regionalization of high
quality special wheat in Shandong province [J]. Journal of
China Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 2002(5): 4?C8.
[11]
Li, Y. G., Yu, Z. W., Liang, X. F., et al. Planting regionalization for high
gluten wheat in Shandong Province [J]. Shandong
Agricultural Sciences, 2001(5): 3?C9.
[12]
Ouyang, Z., Wu, L. F., Wang, C. J., et al. Practice of resource-thrift
modern agriculture in Yucheng, Shandong province [J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2011, 26(4): 383?C389.