Global Change Data Encyclopedia
Hainan Dao, China
Shen, Y. C.1 Liu, C.1* Shi, R. X.1 Han, N. L.2 Chen, H. S.2
1. Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China;
2. School of Politics & Public Administration, Hainan University, Haikou 570228, China
Keywords:Hainan Island; boundary; scope; data encyclopedia
|
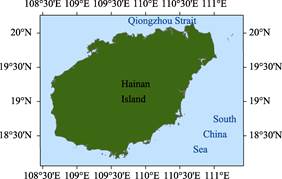
Figure 1 Data Map of Hainan Island (.shp format)
|
Hainan Dao, also called as the Hainan Island (including Hainan Island and its surrounding small rocks, inshore reefs, estuary sand islands), is located in the tropics, with the geolocation of 18°09′34″N-20°09′43″N, 108°36′ 46″E-111°16′25″E[1] (Figure 1). It is separated from Leizhou Peninsula by Qiongzhou Strait at its north, and separated from the People’s Republic of Vietnam by adjacent Beibu Gulf at its west. In the south of the Island, there is the South China Sea with the islands such as Xisha Islands, Zhongsha Islands, and Nansha Islands. It is separated from the Philippines by South China Sea at its east[2].
The total area of Hainan Dao including surrounding small rocks, inshore reefs, estuary sand islands is 34,012.66 km2, and the total coastline is 2,453.79 km. The main island, Hainan Island, has an area of 33,959.44 km2 and a coastline of 2,175.25 km (Table 1), which is the second largest island in China, second only to Taiwan Dao[3]. It belongs to Hainan province, P. R. China.
The Geomorphological characteristic of Hainan Dao is high in the center and low all around. The highest location is Wuzhi Mountain, with the elevation of 1,867 m above sea levle[4]. In addition, the peaks, such as Limu Mountain and Jianfeng Mountain, distributed in the northeast-southwest direction, are located in the southwest-central of the Island. From the highest point of the peak to the coast, the terrain changes from mountains, hills, platforms, plains, coastal zones, and connects with the continental shelf. Restricted by the effect of physiographic stages, the mountain bodies are divided into 6 levels of denudation planation planes, 1,400 m, 800-900 m, 600 m, 500 m, 400 m, and 200-300 m[5]. Under the influence of strata depression or fault, different sizes of basins are widely distributed between mountains and hills, while many alluvial-marine plains with varying widths are distributed along the coast. The climate of Hainan Dao is hot and rainy, long summer and no winter, and obvious dry and wet seasons. The annual average temperature is above 22 oC, with the average temperature higher than 16 oC in the coldest month (January) and annual accumulated temperature (≥10 oC) higher than 8,200 oC. The rain is rich on the Hainan Dao, with the annual average rainfall of 1,500-1,800 mm in most parts of the Island and even 2,000-2,500 mm in the central mountainous area. About 80% of the rainfall falls in the rainy season from May to October, while only about 20% of the rainfall falls in the dry season from November to April of the following year[6]. Vegetation and soil are affected by regional differences in temperature and precipitation and vertical differentiation of mountains. Typical tropical rainforest and seasonal rainforest are developed on hilly platforms with the elevation below 400 m, and the soil is latosol. Vines and parasitic plants are widely distributed in the southeast of the Island, developing into a typical seasonal rainforest landscape[7]. In the southwest of the Island, the rainfall is obviously less, so the drought-tolerant thickets or sparse trees are developed, and the soil is dry krasnozem. The vegetation is evergreen broad-leaved forest in the mountainous area with an elevation of 400-700 m, and the soil is krasnozem. The landscape of mixed evergreen and deciduous broad-leaved forest appeared in the evergreen broad-leaved forest landscape in the mountain area with an elevation of 700-1,200m, and the soil is developed into a yellow soil due to the moisture condition. In the mountains with an elevation above 1,200 m, the temperature is low, the humidity is high, and the wind is strong. Hence, the hilltop scrub and bush wood are grown, and the soil is developed into shrubby-meadow soil[8]. There are mangroves along the coast of Hainan Dao[9].
Table 1 Hainan Dao (Island) and its surrounding small islands
|
Name of island
|
Geo-location
|
Center location
|
Area (m2)
|
Coastline (m)
|
|
Hainan Dao
|
18º9′34″N-20º9′41″N,
108º36′46″E-111º2′32″E
|
19º11′46″N, 109º44′38″E
|
33,959,438,300
|
2,175,246
|
|
Haidian Dao
|
20º2′49″N-20º4′51″N,
110º18′2″E-110º21′24″E
|
20º3′50″N, 110º19′47″E
|
14,408,422
|
16,307
|
|
Xinbu Dao
|
20º3′4″N-20º5′29″N,
110º20′27″E-110º22′30″E
|
20º4′30″N,
110º21′38″E
|
8,169,865
|
20,941
|
|
Dazhou Dao
|
18º39′19″N-18º41′25″N,
110º28′12″E-110º29′39″E
|
18º39′55″N, 110º28′56″E
|
4,108,109
|
13,958
|
|
Ruyi Dao
|
20º3′41″N-20º5′0″N,
110º13′29″E-110º14′49″E
|
20º4′2″N,
110º14′9″E
|
2,718,410
|
12,293
|
|
Haitou
|
19º29′45″N-19º30′38″N,
108º56′15″E-108º57′17″E
|
19º30′14″N, 108º56′45″E
|
2,115,007
|
6,381
|
|
Ximao Zhou
|
18º13′35″N-18º14′44″N,
109º21′48″E-109º22′40″E
|
18º14′6″N,
109º22′12″E
|
1,957,264
|
6,070
|
|
Dongyu Dao
|
19º8′3″N-19º9′4″N,
110º33′35″E-110º34′33″E
|
19º8′35″N,
110º34′5″E
|
1,844,350
|
6,170
|
|
Lecheng Dao
|
19º8′13″N-19º9′1″N,
110º30′53″E-110º31′60″E
|
19º8′38″N,
110º31′24″E
|
1,569,211
|
5,724
|
|
Simapo Dao
|
20º0′4″N-20º1′4″N,
110º22′26″E-110º23′12″E
|
20º0′34″N,
110º22′51″E
|
1,450,627
|
4,943
|
|
Niuqi Zhou
|
18º18′22″N-18º18′59″N,
109º45′16″E-109º46′10″E
|
18º18′43″N, 109º45′44″E
|
1,047,654
|
5,919
|
|
Fenghuang Dao
|
18º13′50″N-18º14′44″N,
109º28′22″E-109º29′40″E
|
18º14′8″N, 109º28′41″E
|
881,305
|
6,256
|
|
Yezhu Dao
|
18º12′26″N-18º13′21″N,
109º39′27″E-109º40′4″E
|
18º13′3″N, 109º39′43″E
|
637,795
|
4,911
|
|
Dongmao Zhou
|
18º12′46″N-18º13′22″N,
109º24′42″E-109º25′5″E
|
18º13′1″N, 109º24′52″E
|
461,734
|
2,985
|
|
Zhouzai Dao
|
18º38′14″N-18º38′36″N,
110º21′10″E-110º21′47″E
|
18º38′25″N, 110º21′27″E
|
445,198
|
3,019
|
|
Nanshi
|
19º54′18″N-19º54′51″N,
111º11′49″E-111º12′15″E
|
19º54′34″N, 111º12′1″E
|
398,556
|
4,147
|
|
Fenjie Zhou
|
18º34′27″N-18º34′59″N,
110º11′33″E-110º12′1″E
|
18º34′43″N, 110º11′47″E
|
394,629
|
4,320
|
|
Beishi Dao
|
19º58′37″N-19º59′12″N,
111º16′2″E-111º16′24″E
|
19º58′55″N, 111º16′12″E
|
338,638
|
3,083
|
|
Xizhou
|
18º10′55″N-18º12′16″N,
109º39′57″E-109º40′51″E
|
18º11′6″N, 109º40′38″E
|
257,107
|
6,798
|
|
Baian Dao
|
18º48′30″N-18º48′58″N,
110º33′53″E-110º34′12″E
|
18º48′45″N, 110º34′3″E
|
255,308
|
2,449
|
|
Jiajing Dao
|
18º38′50″N-18º39′12″N,
110º17′7″E-110º17′21″E
|
18º39′0″N, 110º17′13″E
|
170,372
|
1,913
|
|
Dongluo Dao
|
18º19′26″N-18º19′46″N,
108º59′17″E-108º59′28″E
|
18º19′35″N, 108º59′23″E
|
120,720
|
2,022
|
|
Pingshi Dao
|
19º57′35″N-19º57′51″N,
111º14′55″E-111º15′15″E
|
19º57′42″N, 111º15′6″E
|
118,635
|
2,270
|
|
Hongpai
|
19º58′34″N-19º58′51″N,
109º48′16″E-109º48′38″E
|
19º58′43″N, 109º48′26″E
|
114,800
|
1,891
|
|
Luoting Po
|
19º57′52″N-19º58′3″N,
110º36′32″E-110º36′47″E
|
19º57′58″N, 110º36′40″E
|
93,818
|
1,173
|
|
Dingshi Dao
|
19º57′56″N-19º58′10″N,
111º15′38″E-111º15′55″E
|
19º58′2″N, 111º15′47″E
|
88,699
|
1,601
|
|
Ganzhe Dao
|
18º45′37″N-18º45′49″N,
110º30′2″E-110º30′13″E
|
18º45′43″N, 110º30′7″E
|
84,861
|
1,113
|
|
Dazhou
|
18º13′38″N-18º13′50″N,
109º28′59″E-109º29′11″E
|
18º13′42″N, 109º29′5″E
|
63,221
|
1,130
|
|
Xigu Dao
|
18º19′18″N-18º19′30″N,
108º57′6″E-108º57′14″E
|
18º19′23″N, 108º57′9″E
|
61,217
|
974
|
|
Gangmenshi
|
18º52′57″N-18º53′3″N,
110º31′16″E-110º31′20″E
|
18º52′60″N, 110º31′18″E
|
17,185
|
520
|
|
Chishi Dao
|
19º55′34″N-19º55′41″N,
111º11′52″E-111º11′55″E
|
19º55′37″N, 111º11′53″E
|
14,679
|
593
|
|
Shuangfan
|
19º53′1″N-19º53′5″N,
111º12′43″E-111º12′49″E
|
19º53′4″N, 111º12′46″E
|
11,200
|
503
|
|
Shuangfan Shi (West)
|
18º26′8″N-18º26′11″N,
110º8′24″E-110º8′28″E
|
18º26′10″N, 110º8′26″E
|
7,160
|
336
|
|
Shuangfan Shi (East)
|
18º26′9″N-18º26′12″N,
110º8′27″E-110º8′31″E
|
18º26′11″N, 110º8′29″E
|
5,257
|
344
|
|
Wuzhizhou Dao
|
18º18′57″N-18º18′58″N,
109º46′11″E-109º46′11″E
|
18º18′57″N,
109º46′11″E
|
506
|
87
|
|
Others
|
|
|
8,794,328
|
125,404
|
|
Total
|
|
|
34,012,664,148
|
2,453,793
|
Hainan Dao has a resident population of more than 9 million (9.11 million in 2015[10]), with more than 1 million in Haikou city, the capital of Hainan province[11]. There are several people groups of Han nationality, and besides Han, there are Li, Miao, etc. There are six Li and Miao autonomous counties (Baisha, Changjiang, Ledong, Lingshui, Baoting, and Qiongzhong) on the island. In 2001, the Boao Forum for Asia was held on the Hainan Dao, which became the annual gathering place of the Asian economic forum[12]. Hainan Dao is a suitable region for the tropical agriculture. The main food crops include rice, sweet potato. Cash crops include sugar cane, peanuts, beans, sesame, and tea; economic trees include rubber, coconut, coffee, pepper, betel nut, oil palm, cocoa, cashew nuts, etc.; while tropical fruits include litchi, mango, longan, pineapple, and durian, with abundant yield[13]. Hainan Dao is rich in different types of tourism resources, and has the unique basis and conditions to develop tropical island tourism, mountain tourism, coastal tourism, cruise tourism, and folk tourism[14].
The boundary data of Hainan Dao was developed based on the Google Earth images (2015) and related maps and references. The dataset consists of 15 data files and archived in the .shp[15] and .kmz formats with the data size of 10.2 MB (compressed to 4.0 MB in two data files).
References
[1] Shen, Y. C., Liu, C., Shi, R. X. Boundary of Hainan Island [DB/OL]. Global Change Research Data Publishing & Repository, 2015. DOI: 10.3974/geodb.2015.01.10.V1.
[2] Zheng, D., Yang, Q. Y., Wu, S. H. Physical Geography of China [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2015: 588-594.
[3] Editorial Board of 1??1000000 Map on Land Type in China. Description of E-49 in 1??1000000 Map Land Type in China [M]. Beijing: Surveying and Mapping Press, 1989.
[4] Yuan, J. P., Yu, L. S., Deng, G. Q. Geomorphologic division and classification of Hainan Island [J]. Natural Science Journal of Hainan University, 2006, 24(4): 364-370.
[5] Zeng, Z. X., Zeng, X. Z. Physical Geography of Hainan Island [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1989.
[6] He, D. Z., Zhang, S. L. The regional climate division of Hainan Island [J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 1985, 40(2): 169-178.
[7] Tan, X. D., Liu, Y. L. Biodiversity of Hainan Island and its protection countermeasures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Agriculture, 2007, 27(6): 50-53.
[8] Zou, B. S., Zhang, W. Y. The groups and features of tropical forest vegetation of Hainan Island [J]. Huihaia, 2002, 22(2): 107-115.
[9] Editorial board of Chinese Vegetation. Chinese Vegetation [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1980: 402-410.
[10] Webesite of the People’s Government of Hainan province [OL]. http://www.hainan.gov.cn/hainan/zfsj/xsj.shtml.
[11] Ministry of Civil Affairs of P. R. China. Brief Description of Administration Division of China [M]. Beijing: Sinomap Press, 2016.
[12] Zhou, W., Wang, Z. P. Structural optimization and functional perfection of Boao Forum for Asia [J]. Journal of Nantong University (Social Sciences Edition), 2017, 33(5): 42-48.
[13] Guangzhou Institute of Geography. Natural Resources and Regionalization of Tropical Agriculture in Hainan Island [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1985.
[14] Sinomap Press. Hainan Tourism [M]. Beijing: Sinomap Press, 1994.
Data Computing Environment
[15] ESRI. ArcGIS campus license of Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China.
URL for Data Downloading
http://www.geodoi.ac.cn/WebEn/doi.aspx?Id=203.
Or search through: http://www.geodoi.ac.cn.