Land Use Dataset of the Urban Fringe in Xi??an
(2015)
Wang, B.1
Huang, X. J.1,2,3* Wang, C.1 Hu, K. L.1
1. College of Urban and Environmental Sciences, Northwest
University, Xi'an 710127, China;
2. Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Earth Surface System and Environmental
Carrying Capacity, Xi'an 710127, China
3. Shaanxi Xi??an Urban Forest Ecosystem Research Station,
Xi'an 710127, China
Abstract: The urban fringe
is a transitional area between the urban built-up and rural areas. It is
characterized by an interlaced state of land use and a fragmented landscape
caused by the invasion of urban construction land into agricultural land. This
data set contains Google Earth images that can be used to classify and
interpret Landsat Thematic Mapper (TM) images of the Xi'an urban area and its
adjacent areas in 2015 to obtain land use data. In combination with the spatial
development trend of urbanization in Xi'an, we selected the proportions of
construction land and farmland, and a landscape fragmentation index of each
Jiedao in Xi'an to determine the boundary of the urban fringe, and obtained a
land use data set of the urban fringe in Xi'an (2015). The results showed that
the urban fringe of Xi'an includes 25 Jiedao, belonging to the Baqiao,
Chang'an, Yanta, and Weiyang Districts and Fengdong New Town, and the land use
types were mainly construction land, farmland, forest land, and other land
uses. This data set is stored in .shp format and consists of 14 data files,
with a data volume of 8.11 MB (compressed to one file, 4.78 MB). The research
paper based on this data set was published in Volume 73, No. 6, of Acta
Geographica Sinica (2018)
Keywords: urban fringe; land use; Xi??an; Jiedao
1 Introduction
In recent years, with
China??s rapid urban expansion, the functional space of transportation,
industry, and housing has spread to the suburbs of cities. However, the
increase in the area of urban construction land has mainly occurred due to the
assimilation of farmland into suburban areas, which has resulted in the urban
fringe at the junction of urban and rural areas becoming severely and
profoundly affected by urban spatial expansion[1?C2]. Under this background,
the urban fringe has been deeply affected by continuous spatial reconstruction
and has frequently experienced a functional transformation. It has become the
most unstable and sensitive area of many cities, and is also the region where
urban?Csocial conflicts are particularly prominent. Because of its
transitional, ambiguous, and dynamic characteristics [3], the
boundary of the urban fringe is usually difficult to define accurately, which
hinders the precise governance of cities. Therefore, it is of great
significance to scientifically define the spatial scope of the urban fringe and
grasp the dynamic changes of land use in the urban fringe to maintain a healthy
and orderly urbanization.
As a significant consequence of urbanization, land use change is not only a typical feature of the urban
fringe, but is also an important basis for defining the spatial scope of the
urban fringe area. An interlaced state of land use and a fragmented landscape
caused by the invasion of urban construction land into agricultural land are
the main characteristics of the urban fringe [4]. This data set
takes Xi'an as the research area, and classifies and interprets Landsat TM
images of the Xi'an urban area and its adjacent areas in 2015 to obtain land
use data. By combining this information with the spatial development trend of
urbanization in Xi'an, we selected the proportion of construction land, the
proportion of farmland, and a landscape fragmentation index of each Jiedao in
Xi'an to define the boundary of the urban fringe of Xi'an, and obtained a land
use data set of the urban fringe in Xi'an (2015). This data set not
only provides a method for defining the urban fringe, but also provides a reference
for land use planning and urban development in the study area.
2 Metadata of Dataset
The name, author,
geographical region, data year, data set composition, data publishing and sharing
service platform, and data sharing policy of the land use data set of the urban
fringe in Xi??an (2015) are listed in Table 1.
3 Data Development Method
3.1 Raw Data
The
urban fringe boundary data in this data set are from the Shaanxi Bureau of
Surveying, Mapping and Geoinformation, and land use
data are from Landsat TM images in the Geospatial Data Cloud
(http://www.gscloud.cn)[7] and Google Earth images. All data
are from 2015.
3.2 Algorithm Principle
(1) This data set uses Landsat TM remote sensing images and Google Earth
images as its main data sources. After image
fusion, geometric correction, and image clipping, we overlay the administrative
boundary data of each Jiedao to Landsat TM images
and digitalized the land use status of each Jiedao in Xi'an city and its
adjacent areas using a human-computer interactive visual interpretation method.
We then divided the land use types into four categories: construction land,
farmland, forest land, and other land, and obtained a vector map of land use in
Xi'an City.
(2) Based on the land use data,
we determined the proportion of construction land and farmland in each Jiedao.
Then we converted the vector data of land use into raster data and input it
into Fragstats 4.2 software to calculate the fragmentation index of
construction land and farmland of each Jiedao.
(3) In combination with the
spatial development trend of Xi'an urbanization, land use status,
the proportion of construction land and farmland, and a landscape fragmentation
index of each Jiedao, we defined the boundary of
the urban fringe, and finally obtained a land use data set of the urban fringe
in Xi??an.
Table 1 Metadata summary of the land use data
set of the urban fringe in Xi'an (2015)
|
Entry
|
Description
|
|
Dataset
full name
|
Land use data set of the urban fringe in
Xi'an (2015)
|
|
Dataset
short name
|
LU_UrbanFringe_XiAn
|
|
Authors
|
Wang, B., College of Urban and
Environmental Sciences, Northwest University,
1500633823@qq.com
Huang, X. J., X-9862-2019, College of Urban
and Environmental Sciences, Northwest University, huangxj@nwu.edu.cn
Wang, C., College of Urban and
Environmental Sciences, Northwest University, 592364561@qq.com
Hu, K. L., College of Urban and
Environmental Sciences, Northwest University,
1505566206@qq.com
|
|
Geographical region
|
Xi??an city (33??25¢12²N-34??27¢00²N, 107??24¢00²E-109??29¢24²E)
|
|
Year
|
2015 Data
format .shp Data size 4.78 MB (after compression)
|
|
Data files
|
Boundary data of the urban fringe in Xi??an;
Land use data in the urban fringe of Xi??an
|
|
Foundations
|
National Natural Science Foundation of China (41971178;41401138)??Shaanxi province (SKLESS201807)
|
|
Data publisher
orm
|
Global Change Research Data Publishing
& Repository. http://www.geodoi.ac.cn
|
|
Address
|
No.11A, Datun Road, Chaoyang District,
Beijing 100101, China
|
|
Data
sharing policy
|
Data from the Global Change Research Data Publishing &
Repository includes metadata, dataset (data products), and publications (in
this case, in the Journal of Global Change Data & Discovery). Data sharing policy includes: (1) Data
are openly available and can be free downloaded via the Internet; (2) End
users are encouraged to use Data subject to citation; (3)
Users, who are by definition also value-added service providers, are welcome
to redistribute Data subject to written permission from the GCdataPR
Editorial Office and the issuance of a Data redistribution license; and (4) If Data
are used to compile new dataset, the ??ten per cent principal?? should be followed
such that Data records utilized should not surpass 10% of the new
dataset contents, while sources should be clearly noted in suitable places in
the new dataset
[6]
|
|
Communication and searchable system
|
DOI, DCI, CSCD, WDS/ISC, GEOSS, China GEOSS
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
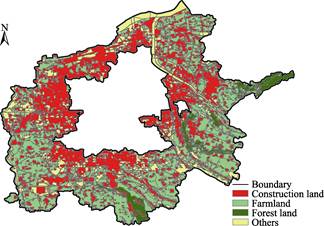
Figure 1 Land use status of the urban fringe in
Xi'an in 2015
|
4 Results
4.1 Composition of Dataset
The land use data set of the
urban fringe in Xi'an (2015) consists of two parts: (1) boundary data of the urban fringe in Xi'an (.shp); and (2) land use data in the urban fringe of Xi'an (.shp). The spatial
distribution results are shown in Figure 1.
4.2 Analysis of Data Results
The urban fringe area of
Xi'an includes 25 Jiedao belonging to the Baqiao, Chang'an, Yanta, and Weiyang
Districts and Fengdong New Town, with a total area of
1425.22 km2. Compared with the core areas that have fully realized
urbanization, these 25 spatial units still have certain amounts of
farmland, and the agricultural and urbanized spaces are intertwined and mixed. Statistical information regarding the land use in each Jiedao
is given in Table 2.
Table
2 Area of different land uses in the urban
fringe in Xi'an??km2??
|
Municipal district
|
Jiedao
|
Farmland
|
Construction land
|
Forest land
|
Others
|
|
Baqiao
|
Hongqi
|
8.29
|
27.36
|
8.38
|
10.67
|
|
Xiwang
|
24.71
|
20.13
|
4.62
|
9.20
|
|
Hongqing
|
32.05
|
24.99
|
22.92
|
6.00
|
|
Dizhai
|
37.18
|
16.80
|
7.64
|
3.15
|
|
Baqiao
|
19.11
|
29.69
|
0.41
|
12.88
|
|
Xinzhu
|
23.59
|
25.45
|
0
|
10.29
|
|
Xinhe
|
37.11
|
23.16
|
0
|
15.78
|
|
Chang'an
|
Weiqu
|
12.92
|
44.09
|
0
|
18.76
|
|
Guodu
|
18.06
|
44.00
|
0.67
|
25.30
|
|
Xiliu
|
38.47
|
10.93
|
0.03
|
2.15
|
|
Duqu
|
36.85
|
12.00
|
0.95
|
7.77
|
|
Dazhao
|
39.93
|
15.10
|
0.94
|
7.86
|
|
Xinglong
|
23.58
|
20.19
|
0.15
|
10.40
|
|
Huangliang
|
20.48
|
6.93
|
0.64
|
0.55
|
|
Wangqu
|
27.88
|
12.94
|
20.38
|
2.39
|
|
Wuxing
|
24.21
|
8.26
|
0.92
|
4.35
|
|
Paoli
|
36.31
|
9.26
|
4.39
|
12.59
|
|
Yanta
|
Dengjiapo
|
0.82
|
16.12
|
0.04
|
6.33
|
|
Yuhuazhai
|
2.63
|
24.88
|
0.28
|
5.68
|
|
Weiyang
|
Liucunbao
|
14.68
|
30.89
|
0.01
|
8.45
|
|
Hancheng
|
2.59
|
32.48
|
0
|
9.24
|
|
Caotan
|
3.78
|
28.70
|
0
|
28.43
|
|
Fengdong New Town
|
Sanqiao
|
2.03
|
39.66
|
0
|
7.25
|
|
Doumen
|
26.69
|
30.31
|
0.38
|
17.98
|
|
Wangsi
|
7.45
|
18.20
|
0.08
|
14.02
|
The main land use types in the urban fringe of Xi'an
in 2015 were farmland and construction land, with an area of 521.40 km2and
572.52 km2, accounting for 38.05% and 41.78% of the total area,
respectively. Dazhao Jiedao had the largest farmland area (39.93 km2).
The farmland area of Hongqing, Dizhai, Xinhe, Xiliu, Duqu, and Paoli Jiedaos
also exceeded 30 km2. However, the area
of construction land in Weiqu, Guodu, LiucunBao, Hancheng, and Sanqiao Jiedaos
exceeded 30 km2. The largest forest land area
was Hongqing Jiedao (22.92 km2). Forest land was also
relatively abundant in Hongqi, Xiwang, Dizhai, and Wangqu Jiedaos. The other land area of Caotan Jiedao was 28.43 km2,
with most of the land being a large water area.
From the perspective of the proportion of land use, the largest proportion of construction land (>80%) was in
Sanqiao Jiedao. The proportion of
construction land in Hongqi, Weiqu, Guodu, Dengjiapo, Yuhuazhai, Liucunbao, and
Hancheng was also over 50%. This indicates that these
areas were strongly influenced by urbanization and were rapidly becoming urban
built-up areas. In contrast, the proportion
of farmland in Huangliang, Xiliu, Wuxing, and Duqu was still over 50%, which
indicates that the urbanization process has been relatively slow due to the
distance from the urban center.
4.3 Description of Data Results
This data set is based on
Landsat TM images, with a resolution of 30 m. The resolution of the images is
slightly coarse. Even with the assistance of Google Earth images, there are
still some errors in the results. In addition, the data set only
classifies land use types into farmland, construction land, forest land, and
others in the interpretation process, the classification of which is
comparatively general. There are still some areas of water and
grassland in the urban fringe, and there are numerous types of construction
land. To determine land use changes in the urban fringe in Xi'an more
intuitively and accurately, multi-period SPOT and Landsat TM images, with
higher resolution, should be used for land use interpretation in the future.
This will enable an assessment of exactly what type of construction land the farmlandhas
been converted into in the urban fringe and will enable the dynamic changes of
land use to be determined, therefore providing a reference for future urban
land planning.
5 Discussion
and Conclusion
The urban fringe is located
between the two systems of the "city" and "country.?? It is the
most sensitive, influential, and rapidly changing area during the process of
urbanization. The most prominent feature of the urban fringe is that
the land use situation is complex and changes rapidly, which makes urban land
use planning difficult. This data set makes use of
Google Earth images to classify and interpret Landsat TM images of the Xi'an
urban area and its adjacent areas in 2015 to obtain land use data. By combining
this information with the spatial development trend of urbanization in Xi'an,
we selected the proportion of construction land and farmland, and a landscape
fragmentation index for each Jiedao in Xi'an to determine the boundary of the
urban fringe, and finally obtained a land use data set of the urban fringe in
Xi'an (2015). From the results, it was apparent that the closer the
Jiedao was to the city center, the more severely it was affected by
urbanization. A large area of farmland in these Jiedaos had been transformed
into urban construction land, and the degree of landscape fragmentation was
also higher. The Jiedaos far from the city center were relatively weakly
affected by urbanization, and still had a high proportion of farmland. The development of this data set provides a method to determine
urban fringe areas. In addition, the data set itself also provides support for
relevant research and urban land use planning in Xi'an.
Author
contributions
Huang, X. J. designed the
development of the data set; Wang, C. and Hu, K. L. collected and processed
data; and Wang, B. wrote the paper.
References
[1]
Gu,
C. L., Chen, T., Ding, J. H., et al.
The study of the urban fringes in Chinese megalopolises [J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 1993, 48(4):
317?C328.
[2]
Peng, J., Ma, J., Yuan, Yuan. Research progress and prospect on the
identification of urban fringe [J]. Progress
in Geography, 2014, 33(8): 1068?C1077.
[3]
Wang, Ha. Y., Zhang, X. C.,
Kang, T. J., et al. Urban fringe
division and feature analysis based on the multicriterion judgment [J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2011,
26(4): 703?C714.
[4]
He, Y. B., Huang, X. J., Zhai,
L. X., et al. Assessment and
influencing factors of social vulnerability to rapid urbanization in urban
fringe: A case study of Xi??an [J]. Acta
Geographica Sinica, 2016, 71(8): 1315?C1328.
[5]
Huang, X. J., Wang, C., Hu, K.
L., et al. Land use data set of urban
fringes in Xi??an (2015) [DB/OL]. Global Change Research Data Publishing &
Repository, 2019. DOI: 10.3974/geodb.2019.04.08.V1.
[6]
GCdataPR
Editorial Office. GCdataPR data sharing policy [OL]. DOI: 10.3974/dp.policy.2014.05
(Updated 2017).
[7] Geospatial Data Cloud site, Computer Network Information Center,
Chinese Academy of Sciences. (http://www.gscloud.cn); Image track number is
P127 / R36. DOI: 10.3974/dp.policy.2014.05.txt