GIES Case Dataset on Yanchi Tan Sheep Arid Grassland in Huamachi
Township, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China
Zhang, M. X.1* Sun, Y. W.2* Li, B.3 Liu, C.4 Wu, G. H.3 Wang, Y. J.1 Yan, R.5 Wang, Z. X.4 Shi, R. X.4 Yu, X. H.6 Bai, Y. J.7
1. College of
Geographical Science and Planning, Ningxia University, Yinchuan 750021, China;
2. Agriculture and Rural Affairs Bureau of Yanchi
County, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region,
Yanchi 751500, China;
3. Ningxia Yanchi
Tanyang Industry Group, Yanchi, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region,
Yanchi 751100, China;
4. Institute of
Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research, CAS, Beijing 100101, China;
5. College of Agriculture,
Ningxia University, Yinchuan 750021, China;
6. Publicity
Department of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, Yinchuan 750001, China;
7. Wanjigou
Village, Huamachi Town, Yanchi County, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region,
Yanchi 751599, China
Abstract: The Huamachi town of Yanchi county, Ningxia Hui autonomous region of
China is located at the border among four provinces (Shaanxi, Gansu, Inner
Mongolia and Ningxia) and is mainly covered with arid grassland. Yanchi Tan
sheep is the National Geographical Indication Product, which plays an
irreplaceable role in the life of local people in Yanchi, Ningxia Hui
autonomous region. Huamachi town is the core habitat (ecological geographical
environment) of Yanchi Tan sheep, which has accumulated the experience of
inheritance significance in the habitat protection and sustainable development
of Tan sheep. The case dataset of Tan sheep of semi-arid grassland in Huamachi
town of Yanchi includes: (1) The dataset of Huamachi town of Yanchi and its
adjacent areas; (2) DEM and slope classification data of Yanchi county; (3) Soil
pH and chemicals in Wanjigou village, Huamachi town, Yanchi county; (4) Yanchi
grassland plant species data; (5) Groundwater chemical data of Wanjigou
village, Huamachi town; (6) Land use and NDVI data of Yanchi county. The
dataset is archived in .shp, .tif, .xls, .png and .docx formats with a data size
of 329 MB (211 MB in compressed) and consists of 74 data files.
Keywords: Ningxia; Yanchi; Tan Sheep;
Huamachi Town, Geographical Indication; GIES; Case 1
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3974/geodp.2021.03.04
CSTR: https://cstr.escience.org.cn/CSTR:20146.14.2021.03.04
Dataset Availability Statement:
The dataset
supporting this paper was published and is accessible through the Digital Journal of Global Change Data
Repository at: https://doi.org/10.3974/geodb.2021.05.09.V1 or
https://cstr.escience.org.cn/CSTR:20146.11.2021.05.09.V1.
1
Introduction
Yanchi
county is located in the east of Ningxia, at the border of Shaanxi, Gansu,
Inner Mongolia and Ningxia and is within 106??33??E-107??47??E and 37??04??N-38??10??N.
The ancestor of Yanchi Tan sheep is the Mongolia sheep, one of the three sheep
breeds in China. After years of natural evolution and artificial breeding, it
has developed its unique features[1].
To preserve Yanchi Tan sheep, various measures have been taken, including
national standard[2] in 1980,
national geographical indication protection in 2016[3], and local
standard in 2020[4]. ??Yanchi Tan sheep Huamachi town arid grassland
case dataset on ecosystem protection and sustainable development??[5] is a new effort and may be used
to study the habitat sustainability.
2 Metadata of the Dataset
The
metadata of the dataset[5] is
summarized in Table 1. It includes the full name, short name, authors,
geographical region, year of the dataset, data format, data size, data files,
foundation, data publisher, address and data sharing policy, etc.
Table 1 Metadata summary of the dataset
|
Items
|
Description
|
|
Dataset full name
|
Yanchi Tan sheep
Huamachi town arid grassland case dataset on ecosystem protection and
sustainable development
|
|
Dataset short
name
|
YanchiTanSheepCase01
|
|
Authors
|
Zhang, M. X.
L-8674-2018, Ningxia University, 1014279339@qq.com
|
|
|
Sun, Y. W.,
Agriculture and Rural Affairs Bureau of Yanchi County, 2321858709@qq.com
Li, B., Ningxia
Yanchi Tanyang Industry Group, Yanchi, Ningxia, 411702569@qq.com
Liu, C.
L-3684-2016, Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research,
CAS, lchuang@igsnrr.ac.cn
Wu, G. H.,
Ningxia YanchiTanyang Industry Group, Yanchi, Ningxia, 911844543@qq.com
Wang, Y. J.
AAO-8514-2021, Ningxia University, wyj8690@163.com
Yan, R., Ningxia University
Wang, Z. X., Institute
of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research, CAS,
wangzx@igsnrr.ac.cn
Shi, R. X., Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural
Resources Research, CAS, shirx@igsnrr.ac.cn
Yu, X. H., Publicity Department of Ningxia
Bai, Y. J., Wanjigou Village, Huamachi Town, Yanchi County, Ningxia
|
|
Geographical
region
|
Yanchi county,
Ningxia, 106??33??55.8??E-107??39??42.1??E; 37??4??49.7??N-38??9??44.6??N
|
|
Year
|
2020 Data
format .shp, .xls,
.tif, .png, .docx
|
|
Data size
|
329 MB (212 MB
after compression)
|
|
|
|
Data files
|
(1) boundary data
of Yanchi county, township and village; (2) DEM and slope data of Yanchi
county; (3) grassland data in Wanjigou village, Huamachi town; (4) grass
types list, Yanchi; (5) groundwater pH and chemicals, Wanjigou village,
Huamachi town; (6) land use and NDVI, Yanchi county
|
|
Foundations
|
Ningxia Natural
Science Foundation of China (2020AAC03114); High Quality
Development Project of Tan Sheep in Yanchi County; Chinese Academy of
Sciences (A99P2010YT)
|
|
Data publisher
|
Global Change Research Data Publishing & Repository,
http://www.geodoi.ac.cn
|
|
Address
|
No. 11A, Datun Road,
Chaoyang District, Beijing 100101, China
|
|
Data sharing
policy
|
Data from the Global Change Research Data Publishing
& Repository includes metadata, datasets (in the
Digital Journal of Global Change
Data Repository), and publications (in the Journal of Global Change Data & Discovery). Data sharing policy includes: (1) Data are openly available and can
be free downloaded via the Internet; (2) End users are encouraged to use Data
subject to citation; (3) Users, who are by definition also value-added service
providers, are welcome to redistribute Data subject to written permission
from the GCdataPR Editorial Office and the issuance of a Data redistribution
license; and (4) If Data are used to compile new
datasets, the ??ten per cent principal?? should be followed such that Data
records utilized should not surpass 10% of the new dataset contents, while
sources should be clearly noted in suitable places in the new dataset[6]
|
|
Communication and searchable system
|
DOI,
CSTR, Crossref, DCI, CSCD, CNKI, SciEngine, WDS/ISC, GEOSS
|
|

Figure 1 Location
of Huamachi town,
Yanchi county,
Ningxia
|
3 Geographical Boundary Data of the
Study Area
The boundary data
of this study include geographic data of Yanchi county and Huamachi town.
This county covers an area of 8,522 km2 including 4 towns, 4
townships, and one street office. Four towns are: Huamachi, Dashuikeng,
Huianbao, and Gaoshawo. Four townships: Wanglejing,
Fengjiegou, Qingshan, Mahuangshan. Huamachi town is located in the northeast
corner of Yanchi, is the capital of Yanchi county. The
town covers an area of 1,531 km2, including 23 administrative
villages, one urban community and 146
natural villages. Of the 35,000 residents, there are 32,000 working
in agriculture sector (Figure 1).
4 Geographical Data
The geographical
data includes DEM and slope, meteorological data, hydrology data, soil data,
land cover data, and grassland data.
4.1 Terrain and Meteorological Data
Yanchi
county lies in the transitional zone from the Loess
plateau in the south to the Maowusu desert in the north (Figure 2). As a
result, the corresponding climate is a transition from semiarid to arid, the
vegetation is the transition from arid grassland to desert, and the land use is
the transition from agriculture to pasture[7].
This transition in geography leads to the diversity of natural resources and
the fragility of ecological environment.
The climate of
Yanchi is continental arid, with four distinct seasons, late spring and early
autumn, long winter and short summer, sufficient sunshine and intense
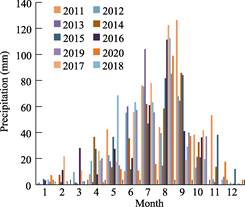
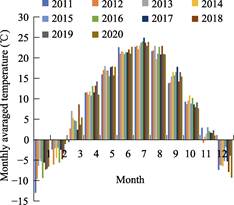
evaporation. According to the records of Yanchi Meteorological Station (2011-2020), the annual average temperature of Yanchi is 7.8 ??C, the extreme high temperature is 38.1 ??C and the extreme low temperature is ‒29.6 ??C, and the day-night temperature difference can reach 20 ??C. The annual sunshine is 2,180-3,390 hours. The annual rainfall is 200-240 mm, mostly concentrated in July, August and September,
accounting for more than 60% of the annual precipitation. The annual
evaporation is about 1,800-2,400 mm,
and is about 10 times of the annual precipitation. The monthly precipitation,
monthly average temperature and monthly sunshine duration in Yanchi from 2011
to 2020 are shown in Figure 3, 4 and 5.
4.2 Groundwater Quality Data
4.2.1 Groundwater Quality Data
Six water quality samplings were conducted in
five villages (Nanwangjiquan, Beiwangjiquan, Lizhaizi,
Wanjigou, and Yangzhaizi villages) and one ecological pasture of
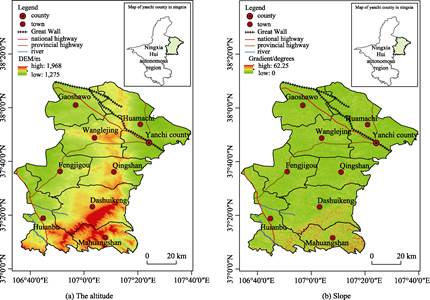
Figure 2 The
altitude and slope of Yanchi county and Huamachi town
|
|
|
|
|
Figure
3 Monthly
precipitation in Yanchi, 2011-2020
|
Figure
4 Monthly
average temperature in Yanchi, 2011-2020
|
|
Tan Sheep Group Company. Water quality
analysis was completed by the water quality
Testing
Center of Ningxia ShuitouYanchi Water Co., Ltd., (Table 2, and Figure 6).
As can be seen from Table 2, groundwater in
the whole region is generally alkaline, with pH value between 7.85 and 8.17,
and the most alkaline places are located in Yangzhaizi and Wanjigou. The
highest groundwater hardness is located in Lizhaizi, which is 1,000.9 mg/L,
belongs to the extra-hard water.
4.2.2 Quality of Water Consumed by Tan
Sheep in Wanjigou
According to the
National standard for groundwater quality (GB/T 14848??2017)[8]
and the comparative analysis of toxicological indicators of groundwater in the
case area, the fluoride
|
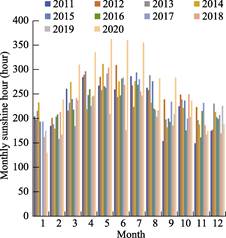
Figure
5 Monthly sunshine
hours in
Yanchi, 2011-2020
|
in five samples (No.2-No.6)
exceeded the standard, the toxicological indicators of the groundwater samples
met the Class III water standard. GB 5749??2006 stipulates that Class III
groundwater is medium in quality, suitable for centralized drinking water,
industrial and agricultural water; and Class IV groundwater is poor, which is
only suitable for agriculture and some industry, and cannot be used as drinking
water without proper treatment (Table 3).
4.3 Main Soil Types and pH
According to the second soil survey in Yanchi
in 1983, the soil in Yanchi can be divided into nine types: lime soil, aeolian
soil, dark loessial soil,
Table 2 Sensory characteristics and
general chemical indexes of groundwater (mg/L)
|
No.
|
Sampling point
|
pH
|
Soluble total solids
|
CaCO3
|
Ammonia nitrogen
|
Fe
|
Mn
|
Cu
|
Zn
|
Chloride
|
Sulfate
|
|
1
|
Nanwangjiquan
|
8.05
|
989
|
400.4
|
0.056
|
<0.003
|
<0.008
|
<0.003
|
<0.015
|
130.6
|
222.1
|
|
2
|
Beiwangjiquan
|
7.85
|
1,740
|
420.4
|
0.086
|
<0.003
|
<0.008
|
<0.003
|
<0.015
|
322.1
|
480
|
|
3
|
Lizhaizi
|
7.85
|
3,356
|
1,000.9
|
0.619
|
<0.003
|
<0.008
|
<0.003
|
<0.015
|
853
|
945.4
|
|
4
|
Wanjigou
|
8.17
|
2,320
|
820.7
|
0.218
|
<0.003
|
<0.008
|
<0.003
|
<0.015
|
438.2
|
580.7
|
|
5
|
Yangzhaizi
|
8.17
|
518
|
280.8
|
0.179
|
<0.003
|
<0.008
|
<0.003
|
<0.015
|
54.1
|
85.9
|
|
6
|
Eco Pasture
|
8.1
|
1,058
|
340.3
|
0.048
|
<0.003
|
<0.008
|
<0.003
|
<0.015
|
210.4
|
290.1
|
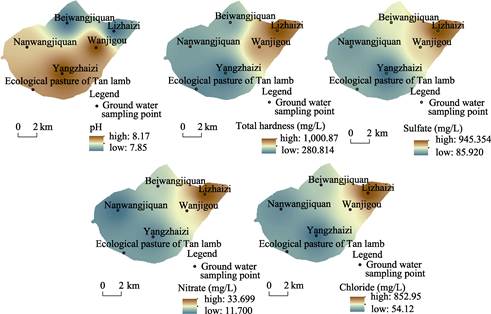
Figure 6 Interpolation of groundwater quality
indexes in Wanjigou village
Table 3 Toxicological
indexes of groundwater in sampling points (mg/L)
|
No.
|
Sampling point
|
As
|
Cd
|
Cr
|
Pb
|
Hg
|
Se
|
fluoride
|
Nitrate (N)
|
|
1
|
Nanwangjiquan
|
<0.001
|
<0.000,25
|
<0.004
|
<0.000,20
|
<0.000,1
|
<0.000,4
|
3.82
|
11.7
|
|
2
|
Beiwangjiquan
|
<0.001
|
<0.000,25
|
<0.004
|
<0.000,20
|
<0.000,1
|
<0.000,4
|
7.13
|
19.3
|
|
3
|
Lizhaizi
|
<0.001
|
<0.000,25
|
<0.004
|
<0.000,20
|
<0.000,1
|
<0.000,4
|
6.96
|
33.7
|
|
4
|
Wanjigou
|
<0.001
|
<0.000,25
|
<0.004
|
<0.000,20
|
<0.000,1
|
<0.000,4
|
4.33
|
22.9
|
|
5
|
Yangzhaizi
|
<0.001
|
<0.000,25
|
<0.004
|
<0.000,20
|
<0.000,1
|
<0.000,4
|
1.58
|
13.1
|
|
6
|
Eco Pasture
|
<0.001
|
<0.000,25
|
<0.004
|
<0.000,20
|
<0.000,1
|
<0.000,4
|
5.13
|
15
|
|
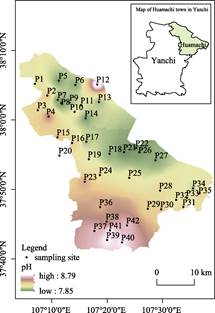
Figure 7 Soil pH in huamachi town, Yanchi
|
saline soil, fresh soil, meadow soil,
heap-bed soil, bobby soil and bare rock. In this study, 40 sample points were
chosen in Huamachi, and the soils in sampling points are lime soil, saline soil
and aeolian sand soil. First, GPS is used to record the geographical locations
of sampling points. Second, removed about 10 cm of surface soil, and cleaned up
all organic impurities in the soil, such as leaves and roots. Third, the ZD-18
instrument was used to insert the metal probe into the soil vertically and
clockwise to about 8-10 cm,
and the soil was compacted evenly around the probe to make the soil fully
contact with the probe. After the numerical value was stabilized, the readings
were recorded (Figure 7). Figure 7 shows that the soil pH in Huamachi was high
in the south and low in the north.
4.4
Unique Grassland Resources
4.4.1 Plant Types: 173 Species from 39 Families and 118 Genera
There are
four types of grassland in Yanchi, including dry steppe grassland, desert
grassland, sand vegetation grassland and halophyte vegetation grassland. There
are 175 species of natural plants, which belong to 39 families, and most of
them are forage plants. Among them, 12 kinds of plants such as licorice and
bitter beans are included in the pharmacopoeia, and 4 kinds of plants such as
green bristle grass are used for folk medicine (Table 4).
4.4.2 Land Use and Land Cover (NDVI) in
Huamachi Town
(1) Land use in
Huamachi town
The land cover and
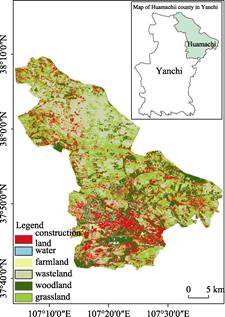
land use map of Huamachi are produced based on Sentinel-2 L2A data[9]. Land use consists of six
types, including construction land, water, cultivated land, woodland and
grassland (Figure 8). The grassland accounted for 30.24% of the total area of
Huamachi.
(2) Land cover
(NDVI) in Huamachi town
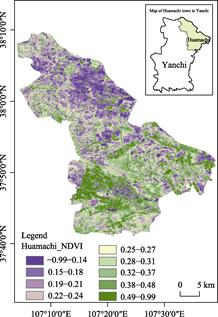
Based on the
Sentinel-2 data, NDVI for five-scenes from September 8, 2020 (spatial
resolution of 10 m) were calculated and synthesized using Equation (1) (Figure
9).
 (1)
(1)
where NIR is the near-infrared
band (Band8 in Sentinel-2); R is the
red band (Band4 in Sentinel-2). The statistics show that NDVI of Huamachi in
September 2020 is between 0 and 0.99, of which, NDVI above 0.21 accounts for 65.77% of the total area.
Table
4 Statistics of families, genera and
species of natural plants in Yanchi
|
No.
|
Families
|
No. of genera
|
No. of species
|
No.
|
Families
|
No. of genera
|
No. of species
|
|
1
|
Leguminosae
|
18
|
33
|
21
|
Euphorbiaceae
|
1
|
2
|
|
2
|
Gramineae
|
18
|
30
|
22
|
Paeoniaceae
|
1
|
2
|
|
3
|
Chenopodiaceae
|
12
|
14
|
23
|
Solanaceae
|
1
|
1
|
|
4
|
Compositae
|
10
|
20
|
24
|
Rutaceae
|
1
|
1
|
|
5
|
Rosaceae
|
6
|
11
|
25
|
Violaceae
|
1
|
1
|
|
6
|
Caryophyllaceae
|
4
|
4
|
26
|
Oleaceae
|
1
|
1
|
|
7
|
Ranunculaceae
|
4
|
4
|
27
|
Verbenaceae
|
1
|
1
|
|
8
|
Papaveraceae
|
4
|
4
|
28
|
Sapindaceae
|
1
|
1
|
|
9
|
Cruciferae
|
4
|
4
|
29
|
Arnebiaceae
|
1
|
1
|
|
10
|
Zygophyllaceae
|
3
|
4
|
30
|
Tamaricaceae
|
1
|
1
|
|
11
|
Polygonaceae
|
2
|
4
|
31
|
Polygalaceae
|
1
|
1
|
|
12
|
Cyperaceae
|
2
|
2
|
32
|
Rhamnaceae
|
1
|
1
|
|
13
|
Labiatae
|
2
|
2
|
33
|
Oxalidae
|
1
|
1
|
|
14
|
Convolvulaceae
|
2
|
2
|
34
|
Pedaliaceae
|
1
|
1
|
|
15
|
Scrophulariaceae
|
2
|
2
|
35
|
Loniceraceae
|
1
|
1
|
|
16
|
Crassulaceae
|
2
|
2
|
36
|
Campanulaceae
|
1
|
1
|
|
17
|
Liliaceae
|
1
|
3
|
37
|
Amaranthaceae
|
1
|
1
|
|
18
|
Ephedracaea
|
1
|
3
|
38
|
Moraceae
|
1
|
1
|
|
19
|
Asclepiadaceae
|
1
|
2
|
39
|
Santalaceae
|
1
|
1
|
|
20
|
Iridaceae
|
1
|
2
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total
|
|
|
|
39
|
|
118
|
173
|
|
|
|
|
Figure 8 Land use type of Huamachi town
|
Figure 9 NDVI of Huamachi town
|
5 Variety Data of Yanchi Tan Sheep
5.1 Identification (Authentication) Standard
of Yanchi Tan Sheep
Yanchi Tan sheep is
a breed for both its skin and meat products, and the identification of this
breed has been included in national and local standards. According to the
national standard GB/T 2033??2008 and the local standard geographical
indications of Ningxia Hui autonomous region??Yanchi Tan sheep DB64/T 1545??2020[4],
Yanchi Tan sheep has a medium build, strong constitution, good combination of
all parts of the body, slightly raised nose bridge, and with three kinds of
ears: large, medium and small. Rams have spiral horns extending outward; ewes
are usually have no or small horns. The back waist is straight, the chest is
deeper, the limbs are straight and the hooves are solid. The tail root is wide,
the tail tip is fine and round, and it is inverted long triangle and droops
over the hock. Body hair color is pure white, most of
the head have brown, black, or yellow hair spots (Figure 10).
|

|

|

|
|
Yanchi Tan sheep (ram)
|
Yanchi Tan sheep (ewe)
|
35?C45 days old lamb
|
Figure 10 Yanchi
Tan Sheep: Rams, Ewes and 35?C45 days old lambs
According to the former State Administration of Quality Supervision,
Inspection and Quarantine, the Genaral Administrtion of Quality Supervision,
Inspeiction and Quarantine of P. R. China, the protected area of the
geographical indication product is limited to the administrative
department of eight towns in Yanchi county within the
administrative area (Figure 1).
5.2 The Mutton Product Standards of Yanchi
Tan Sheep
The quality of
mutton product from Yanchi Tan sheep is guaranteed by a series of
specifications and standards. Specifically, items 15-27 in
Table 5 cover a wide range of fields regarding mutton quality, from carcass
classification to product delivery.
5.3 Product Standards of Tan Sheep Fur and
Fur of Lambs
Because of its soft
texture and light and strong leather board, the leather of Tan sheep is the
best material for making leather clothes and leather goods. The fur of lambs is
produced about one month after birth (35-45 days), and the length of the wool strand reaches 7-8 cm. The release standard and the fur products of Tan sheep have
been listed as the local standard of Ningxia Hui autonomous region (DB64/T
687??2011). The fur of lambs has strict localities as Tan sheep (item 28 in
Table 5).
6 Social Infrastructure for
Yanchi Tan Sheep Development
The total
population in Yanchi is about 159,200, with 81,822 living in towns and 77,303
in villages. There are 4,500 Hui minorities, accounting for 2.6 percent of the
county??s population. In 2020, the per capita disposable income of farmers is
13,922 Yuan, more than 50% comes from the tan sheep
industry. The government, enterprises, herdsmen, technology and media in Yanchi
have coordinated to protect the habitat of Yanchi Tan sheep using following measures.
6.1 Preservation of Fine Varieties
Yanchi is the home
to Tan sheep in China. For a long time, Yanchi Tan sheep is closely related to
local people??s life, and forms the only germplasm resources. It is the
consensus of all stakeholders in Yanchi to protect the fine quality of Tan
sheep. From June 8 to 10, 2020, President XI Jinping inspected Ningxia, and
made comment about Tan sheep, ??Tan sheep has good quality and has its own
special flavor, and we should get it well preserved.??.
6.2 Protection of Intellectual Property
|

Figure 11 Trade
mark of Yanchi Tan sheep
|
Geographical
indication products are a kind of intellectual property. Yanchi Tan sheep has
registered geographical indication products and are also the precious
intellectual property of Yanchi people. The government and enterprises of
Yanchi attach equal importance to the protection of intellectual property and
product quality. Specific measures include:
(1) Raising the awareness of intellectual
property rights, registered the trademarks of geographical indication
In 2005, ??Yanchi Tan sheep?? (Class 29,
registration number: 3334050) was registered by the State of Trademark
Administration as a certification trademark of geographical indications to
prove the specific quality and origin of ??Yanchi Tan Sheep??. In 2008, the
Ministry of Agriculture awarded Yanchi Tan sheep ??Agricultural Geographical
Products??; In 2016, the General Administration of Quality
Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine awarded Yanchi Tan sheep ??National
Geographical Indications Protection Product??. Thus, Yanchi Tan sheep has the
exclusive trademark right under legal protection (Figure 11).
(2) Implementation of the Trademark of
Geographical Indication Products of Yanchi Tan Sheep
In 2021, the government of Yanchi issued
measures to administrate the Trademark of geographical indications products of
Yanchi Tan sheep. The measures stated clearly that ??Yanchi Tan Sheep?? is a collective
Trademark of Geographical Indications Products, whoever wants to use this
trademark need to apply for it, get the approval from trademark registrant, and
sign the trademark use contract. Without the permission of the trademark
registrant, no organization or individuals may use it.
(3) Inspection of law enforcement to
protect the exclusive right of ??Yanchi Tan Sheep?? trademark.
Governments at all levels in Ningxia
carried out rectification actions on the use of the registered trademark of
??Yanchi Tan Sheep??, and banned the actions of deceiving consumers by illegally
using the geographical indications of ??Yanchi Tan Sheep??. The intellectual
property rights of trademark registrants and the legitimate rights and
interests of consumers of ??Yanchi Tan Sheep?? will be effectively safeguarded.
6.3 Standardization of Management
A
series of standards have been issued for the geographical indication products
of Yanchi Tan sheep. The standardization of Yanchi Tan sheep management is an
important guarantee for the protection of Yanchi sheep species, ecological and
geographical environment, and the interests of herdsmen. The 28 standard and
technical Specifications of the ??Yanchi Tan Sheep?? production are listed in
Table 5.
6.4 The Government Provided Ecological Compensation
for Grassland Protection
To
restore high-quality pastures, the government has issued a grazing ban policy.
In 2020, 95,964 ha of grassland received ecological compensation in Huamachi
town. Yanchi county provided the ecological compensation of 112.5 Yuan/ha to
implement the forbidding grazing policy, 10.8 million Yuan in total and
benefiting 8,573 herdsmen.
6.5 Roles Played by Enterprises
Ningxia Yanchi Tan Sheep
Industry Development Group Co., Ltd. is a wholly state-owned
Table 5 Standard and Technical
Specifications of Yanchi Tan Sheep Management
|
Item
|
Standard
and technical specifications
|
Standard*
|
|
1
|
Tan sheep (GB/T 2033??2008)
|
NS
|
|
2
|
Geographical indication products??Yanchi Tan sheep
(DB64/T 1545??2020??
|
LS
|
|
3
|
Standard for sheep farm construction (DB64/T 749??2012)
|
LS
|
|
4
|
Specifications for the
stabling of Tan sheep (DB64/T 845??2013)
|
LS
|
|
5
|
Specifications for ewe Tan
sheep in the house (DB64/T 939??2013)
|
LS
|
|
6
|
Specifications for high
frequency breeding of Tan sheep in house (DB84/T 1480??2017)
|
LS
|
|
7
|
Specification for Yanchi Tan sheep production- mutton
(DB64/T 1232??2016)
|
LS
|
|
8
|
Specification for early supplementary feeding of lambs
(DB64/T 1619??2019)
|
LS
|
|
9
|
Specification for lamb fattening (DB64/T 846??2013)
|
LS
|
|
10
|
Specification for total mixed ration and mixed feeding
for Tan sheep (DB6A/T 1476??2017)
|
LS
|
|
11
|
Specification for silage preparation (DB64/T 104??2013)
|
LS
|
|
12
|
Specification for processing and modulation of forage
enveloped silage (DB64/T 752??2012)
|
LS
|
|
13
|
Specification for sheep farming disease prevention and
control (DB3207/T 116??2018)
|
LS
|
|
14
|
Specification for immunization of sheep small ruminant
pest (DB64/T 1604??2019)
|
LS
|
|
15
|
Specification for Yanchi Tan Sheep Slaughter house
(T/TYXH 02??2017)
|
LS
|
|
16
|
Determination and Carcass Classification of Yanchi Tan
Sheep (DB64/T 1084??2015)
|
LS
|
|
17
|
Practice for PCR-mtDNA Identification of Pure Tan Sheep
(DB64/T 1638??2019)
|
LS
|
|
18
|
Grading Standard for Meat Carcass of Tan Sheep (DB64/T
747??2012)
|
LS
|
|
19
|
Specification and Standard for Segmentation of Yanchi
Tan Sheep Mutton (T/TYXH 01??2017)
|
LS
|
|
20
|
Specification for Lamb Segmentation (NYT1564??2007)
|
LS
|
|
21
|
Specification for Transport and Distribution of Yanchi
Tan Sheep (T/TYXH 04??2017)
|
LS
|
|
22
|
Specification for Sales Zone of Yanchi Tan Sheep
(T/TYXH 03??2017)
|
LS
|
|
23
|
Stir-fried of Yanchi Tan Sheep Lamb Mutton (T/TyxH
06??2017)
|
LS
|
|
24
|
Chunks of Yanchi Tan Sheep Mutton (T/TyxH 07??2017)
|
LS
|
|
25
|
Stewed Yanchi Tan Sheep Mutton (T/TYXH 08??2017)
|
LS
|
|
26
|
Hand-Grab Yanchi Tan Sheep Mutton (T/ TyxH 09??2017)
|
LS
|
|
27
|
Steamed Yanchi Tan Sheep Mutton (TyxH 10??2017)
|
LS
|
|
28
|
Specification for fur products of Yanchi Tan sheep
(DB64/T 687??2011)
|
LS
|
* NS= National
standard; LS=Local standard (Ningxia).
Table 6 Subsidy from Ningxia Yanchi Tan
sheep industrial development group in 2019
|
Batch
|
Towns
|
Villages
|
Natural village
|
Subsidy number
|
Subsidy standard (Yuan/Sheep)
|
Subsidy amount (Yuan)
|
|
1
|
8
|
74
|
213
|
51,246
|
30
|
1,537,380
|
|
2
|
8
|
52
|
161
|
23,564
|
30
|
706,920
|
|
3
|
8
|
61
|
189
|
21,854
|
30
|
655,620
|
|
4
|
8
|
70
|
206
|
23,009
|
30
|
690,270
|
|
5
|
8
|
35
|
68
|
6,921
|
30
|
207,630
|
|
6
|
8
|
85
|
241
|
73,243
|
30
|
2,197,290
|
|
7
|
8
|
32
|
103
|
21,396
|
30
|
641,880
|
|
Total
|
|
409
|
1,181
|
221,233
|
|
6,636,990
|
enterprise established by the government of Yanchi county in 2017. It is an
industrial enterprise of Tan sheep and serves multiple functions: preservation,
purchase, processing, storage, sales and promotion of Yanchi Tan sheep. At
present, the company has a slaughtering factory with a capacity of 300,000, and
has 5,000 sheep in the ecological pastures. In addition, the company
facilitates scientific research, establishes species germplasm bank, help to
diminish various risks. To protect Yanchi Tan sheep species and its genetic
germplasm resources, Ningxia Yanchi Tan Sheep Industry Group Co., Ltd.
established series of measures, a demonstration farm, and a monitoring system.
Demonstration of new technology and
management is an integral part of the Ningxia Yanchi Tan Sheep Industry
Development Group, which covers wide areas. Meet the volatile market resulted
from various factors is another challenge. For example, in 2019, the company
gave each sheep a subsidy of 30 Yuan to enhance farmers?? capacity to meet the
unstable market, with a total subsidy of more than 6 million Yuan (Table 6).
During COVID -19 outbreaks in 2020, the company set
up a trading service platform to help farmers sell their sheep at a fare price,
and meanwhile help farmers buy small lamp.
7 Summary
Persistence
of ??Yanchi Tan Sheep?? as a national geographic indication product benefits from
two factors: the unique, irreplaceable ecological environment (habitat) in
Yanchi, and the well-developed social infrastructure??the engagement of all
stakeholders from individual farmers to relevant companies to local
governments. The development of ??Yanchi Tan sheep Huamachi town arid grassland
case dataset on ecosystem protection and sustainable development?? is a new
effort in this direction. This dataset will promote Yanchi Tan sheep industry
in Ningxia to develop in terms of more scientific approach, more efficient management,
more delicious and safer products. The key takeaways from the development of
this case dataset is: development must adapt to local conditions; respect
geographical tradition; the integration of variety, quality, brand promotion
and reputation; the integration of herdsmen, enterprises, government,
academics; and the coordination of information flow, logistics, and people
flow. While Yanchi Tan sheep has its unique feature, it is also a section in a
broader spectrum of worldwide geographic indication sheep product[10].
There are still many issues to be solved, such as the relationship between
water, soil, grass and air and the quality of Yanchi Tan sheep, and the breed
protection and quality inheritance of Yanchi Tan sheep.
Author Contributions
Liu,
C. and Yu, X. H. made the overall design of the original ecological environment
protection and sustainable development case study of Yanchi Tan sheep in
Huamachi town, Yanchi county, and hosted a field seminar on the case in January
2021.Yu, X. H., Sun, Y. W., Li, B., Wu, G. H., Liu, C. and Zhang, M. X.
completed the field investigation, and Zhang, M. X. designed the data set
framework; Wang, Y. J., Zhang, M. X. developed the land use data. Sun, Y. W.,
Li, B., Wu, G. H. and Zhang, M. X. analyzed water, plants, and soil data, Wang,
Z. X. provided data processing technology and Shi, R. X. classified elevation
data, Shi, R. X. finalized the dataset, Wang, Y. J. processed data and
completed the thesis draft, Liu, C. adjusted the data structure and data
results, revised the Chinese version of the data paper, Wang, Y. J. and Zhang,
M. X. translated the paper into English, and Liu, C. and Wang, Z. X. proofed
the English version.
Acknowledgements
The
team members who assisted in the field investigation are: Ma, R. Y., Minister
of Yanchi Publicity Department; Li, R., Deputy Minister of Yanchi Publicity
Department; Jin, J. R., chairman of Ningxia Tan Sheep Group, Li, Y. L., Deputy
General Manager of Ningxia Tan Sheep Group; Zhang, H. M., Institute of Space
and Space Information Innovation, CAS; Yan, S., Project Assistant of Key
Laboratory of Resource Utilization and Environmental Restoration, Institute of
Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research, CAS.
Conflicts
of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
[1]
Liang, Y., Min, Q. W. Study on the conservation and
utilization of the important agricultural heritage systems in Ningxia [J]. Study on Natural and Cultural Heritage,
2019, 4(11): 96‒100.
[2]
General Administration of Quality Supervision,
Inspection and Quarantine of P. R. China; China National Standardization
Administration Committee. Tan sheep (GB/T 2033??2008) [S].
[3]
Local standards of Ningxia Hui autonomous region.
Geographical indication product, Yanchi Tan sheep (DB64/T 1545??2020) [S]. 2020.
[4]
General Administration of Quality Supervision,
Inspection and Quarantine of P. R. China. Announcement on approving the
protection of geographical indication products for Gannan tea oil and other products
(No. 9, 2016) [OL]. https://dlbzsl.hizhuanli.cn:8888/Product/Detail/468.
[5]
Zhang, M. X., Sun, Y. W., Li,
B., et al. Yanchi Tan sheep Huamachi
town arid grassland case dataset on ecosystem protection and sustainable
development [J/DB/OL]. Digital Journal of
Global Change Data Repository, 2021.
https://doi.org/10.3974/geodb.2021.05.09.V1. https://cstr.escience.org.cn/CSTR:20146.11.2021.05.09.V1.
[6]
GCdataPR Editorial Office. GCdataPR data sharing
policy [OL]. https://doi.org/10.3974/dp.policy.2014.05 (Updated 2017).
[7]
Zhang, K. B., Li, R., Hou, R. P., et al. Study on plant diversity of
different control measures of desertification in Yanchi county, Ningxia [J]. Science of Water and Soil Conservation,
2004(4): 66-72.
[8]
General Administration of Quality Supervision,
Inspection and Quarantine of P. R. China; China National Standardization
Administration Committee. Standard of groundwater quality (GB/T 14848??2017) [S]. Beijing: Standards
Press of China, 2017.
[9]
EU Copernicus
Programme, Sentinel-2 L2A data website [DB/OL].
https://scihub.copernicus.eu/dhus/#/home.
[10]
Erasmus,
S. W., Muller, M., Hoffman, L. C. Authentic sheep meat in the European Union:
factors influencing and validating its unique meat quality [J]. Journal of the Science of Food and
Agriculture, 2017, 97(7): 1979.